Table of Contents
Last update on
Running your own website is a complex undertaking. You have to become knowledgeable in many different areas, from web design over security to performance. Part of that is ensuring the technical SEO of your WordPress website is in order.
Here’s the problem: you might be unsure if that’s the case for your website. You might not even be sure what exactly technical SEO is. That’s precisely why we have put together this detailed guide.
Below, you’ll not only learn what’s part of technical SEO but also how to apply this knowledge to your WordPress site. We’ll explain every piece in detail, describe how to know if your site has a problem in each area, and possible ways of fixing it.
What is Technical SEO (And How Is It Different)?
First things first, what exactly is technical SEO? Commonly, when people think of search engine optimization, they imagine keyword research, content creation, backlinks, etc. And that’s definitely part of it, however, it’s not what technical SEO is about.
Instead, its role is to enable search engines to read (i.e. crawl) and understand (index) your website content to (hopefully) secure positive search rankings for relevant keywords. To do so, technical SEO works on optimizing your website’s infrastructure and underlying code. That includes things like site speed, mobile-friendliness, site architecture, and server files, as well as on-page SEO, image optimization, security, and accessibility.
In short, technical SEO lays the foundation for all other parts of SEO. Because even if you create the best content the world has ever seen, if your site is configured to prevent search engines from finding and indexing it, nobody will ever know.
All clear so far? Then let’s delve into specifics.
1. Build a Great Foundation
At the bottom rung of technical SEO your hosting. The server containing your website has a huge impact on overall site quality, especially performance and downtime. If your site is struggling in these areas, this is the first thing to look at.
We have a number of useful resources on this topic:
- 7 Questions to Ask When Choosing Web Hosting
- Best WordPress Hosting Services for Small Businesses and Blogs
- Shared vs VPS vs Dedicated vs Cloud Hosting
Another important factor is your theme. It not only controls your site’s design but also its underlying code. For that reason, use one that’s SEO and speed-optimized. Here, too, you can check the following articles:
- How to Choose the Best WordPress Theme For Your Website
- The 10 Fastest WordPress Themes
- The 8 Fastest WooCommerce Themes
- 10 Best and Fastest WordPress Themes for Blogs
Finally, keep the number of plugins on your WordPress site to a minimum.
2. Test and Improve Your Website’s Performance
Website speed is a crucial part of technical SEO. It affects both ranking and usability. So much so that Google introduced Core Web Vitals, which specifically measure important parts of page performance.
The first step to improve site performance is to speed test your website. Tools like PageSpeed Insights will give you a detailed list of problems and improvements.
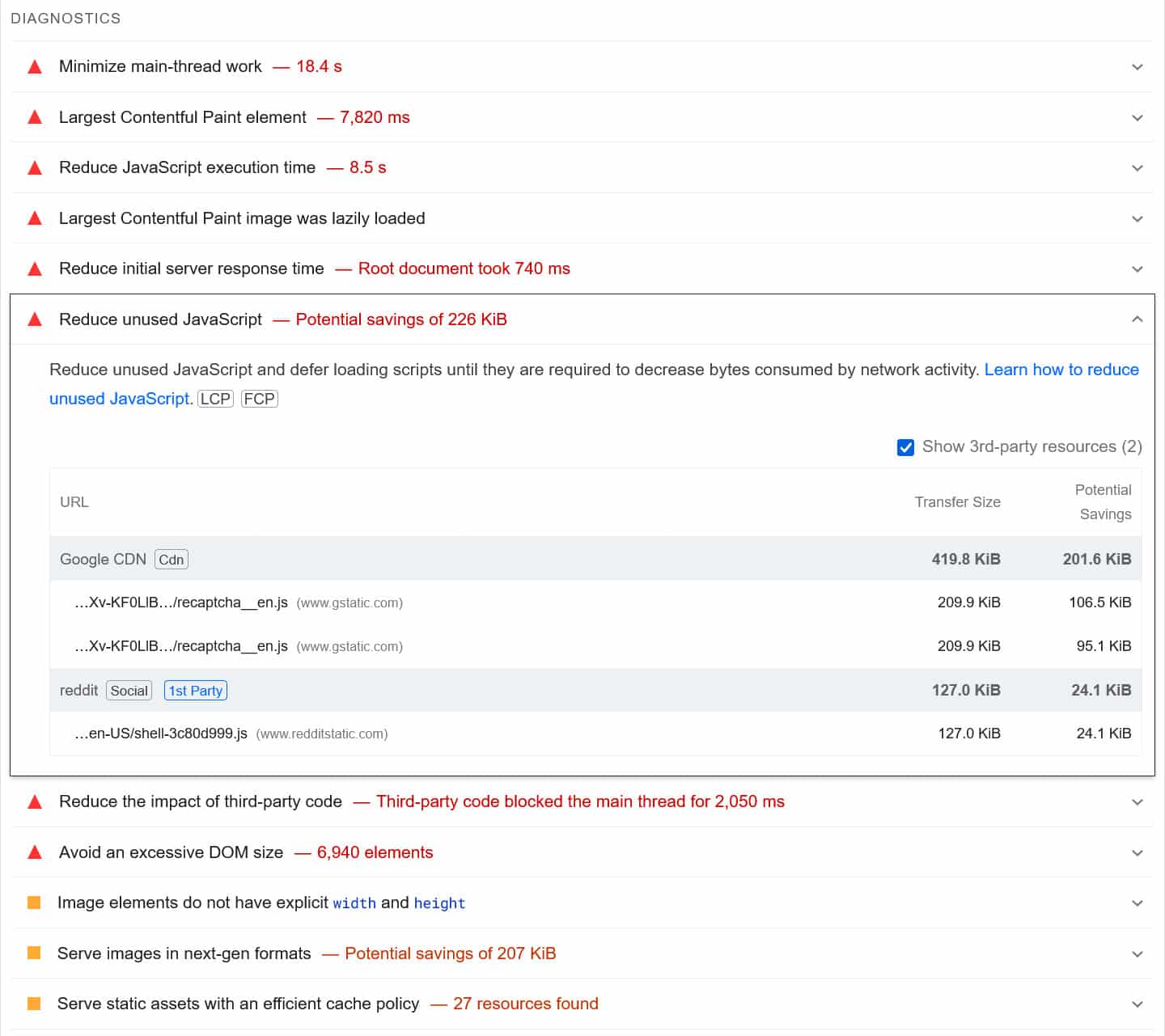
There are many ways to address performance issues, such as caching, minifying CSS and JavaScript files, or using a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
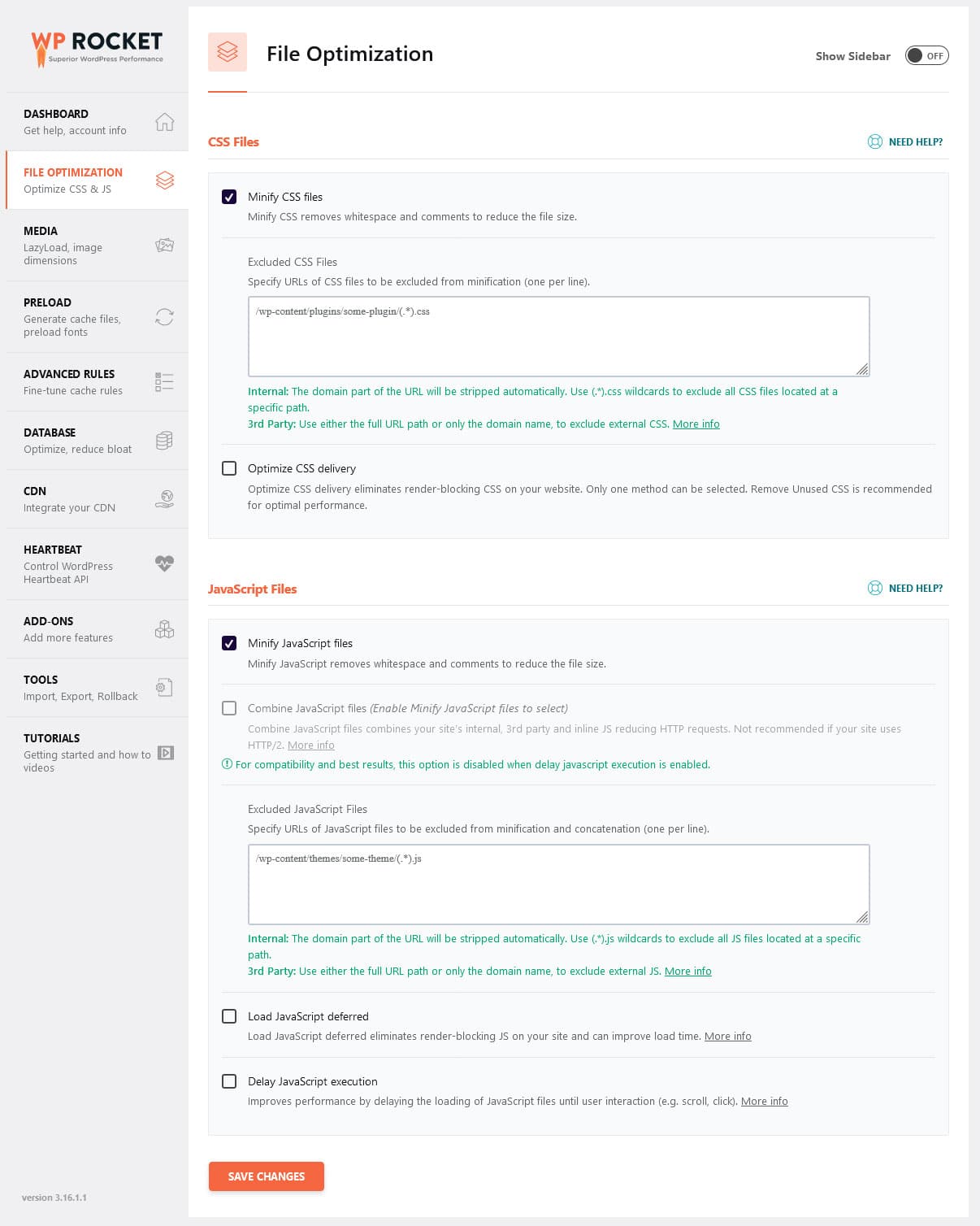
If you feel out of your depth doing this by hand, you can alternatively use a performance plugin like WP Rocket. It has all the necessary features, such as:
- Caching, including for mobile devices
- Lazy loading for images and videos
- Minifying and deferring render-blocking resources
- Preloading cache, links, external files, and fonts
- Database optimization
Even better, a lot of optimization happens automatically, so your site will get faster just by switching the plugin on. This includes browser and server caching, GZIP compression, optimization for images above the fold (since those are usually the LCP element), and a number of smaller improvements. Finally, WP Rocket has a super easy-to-use interface that allows you to make sweeping changes with just a few mouse clicks.
3. Make Sure Your Site Is Mobile Friendly
More people use mobile devices to access the web than desktop computers. As a consequence, Google switched to a mobile-first index in 2018. That means it looks at the mobile version of your website to determine its ranking. Consequently, optimizing your WordPress site for mobile users is definitely part of technical SEO.
If you followed along, you have already taken the first steps to choose a responsive theme and optimize performance. To find any other issues, run your site through a mobile-friendliness test, such as the one by Bing.
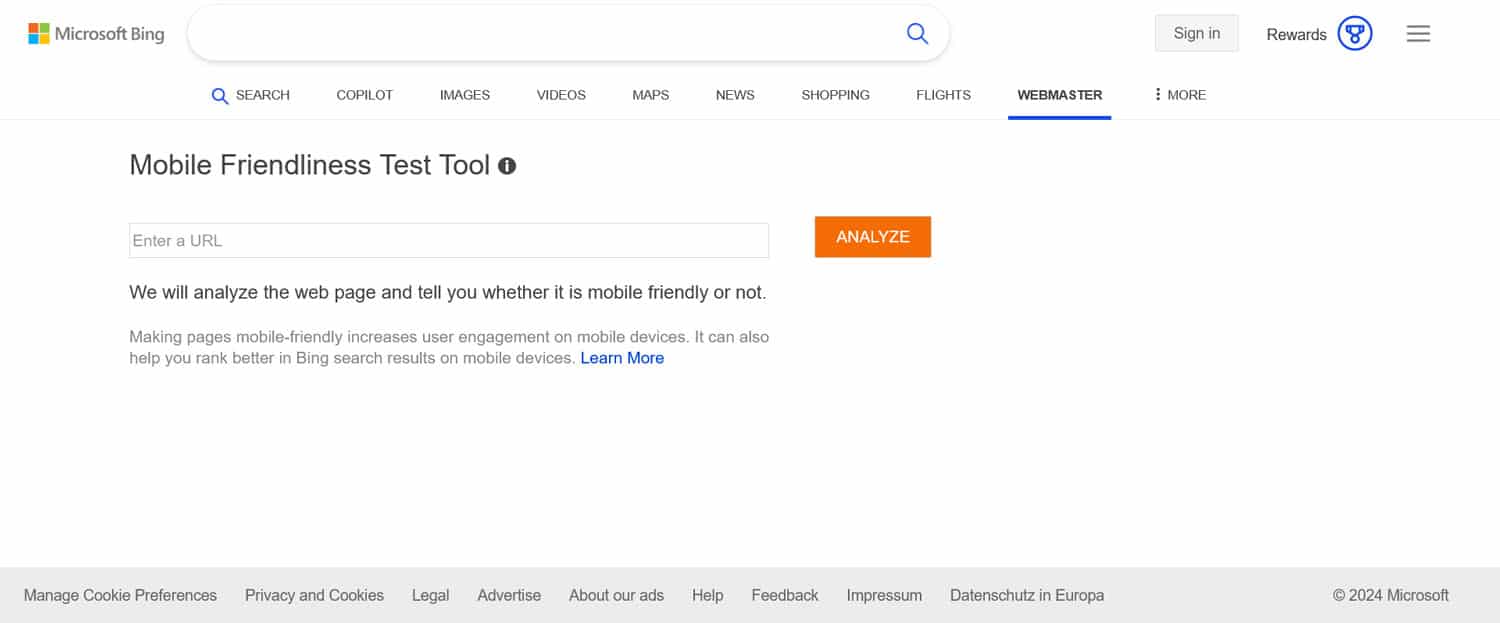
It will tell you, for example, if your text is large enough to read and button sizes sufficient to tap.
4. Ensure Your Site Is Crawlable
With the basics out of the way, it’s time to get a bit more technical. The first thing to check is whether your site can be crawled and thus appear in search engines. One of the easiest ways to do that is to type site:yoururl.com into Google. This shows you all your content that’s in the search engine’s index.
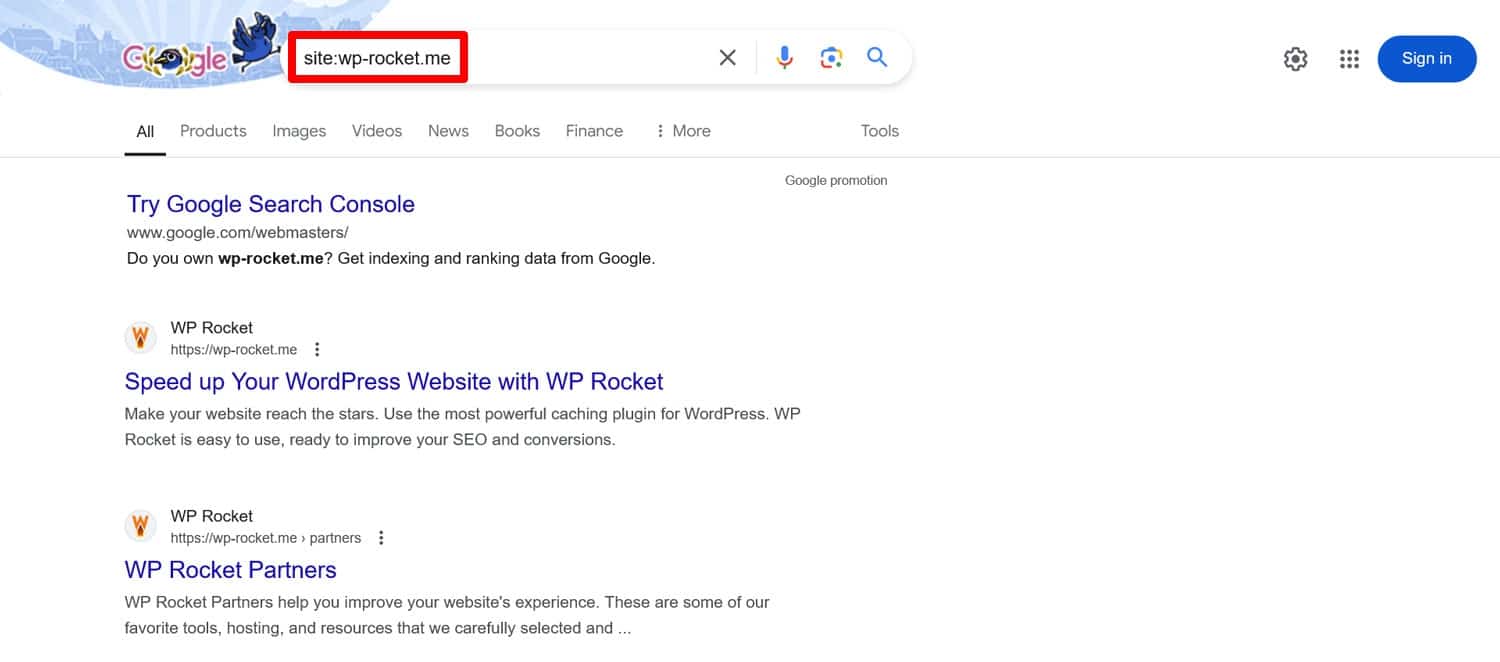
If you can see anything, congratulations, your site is indexable. What a relief, right?
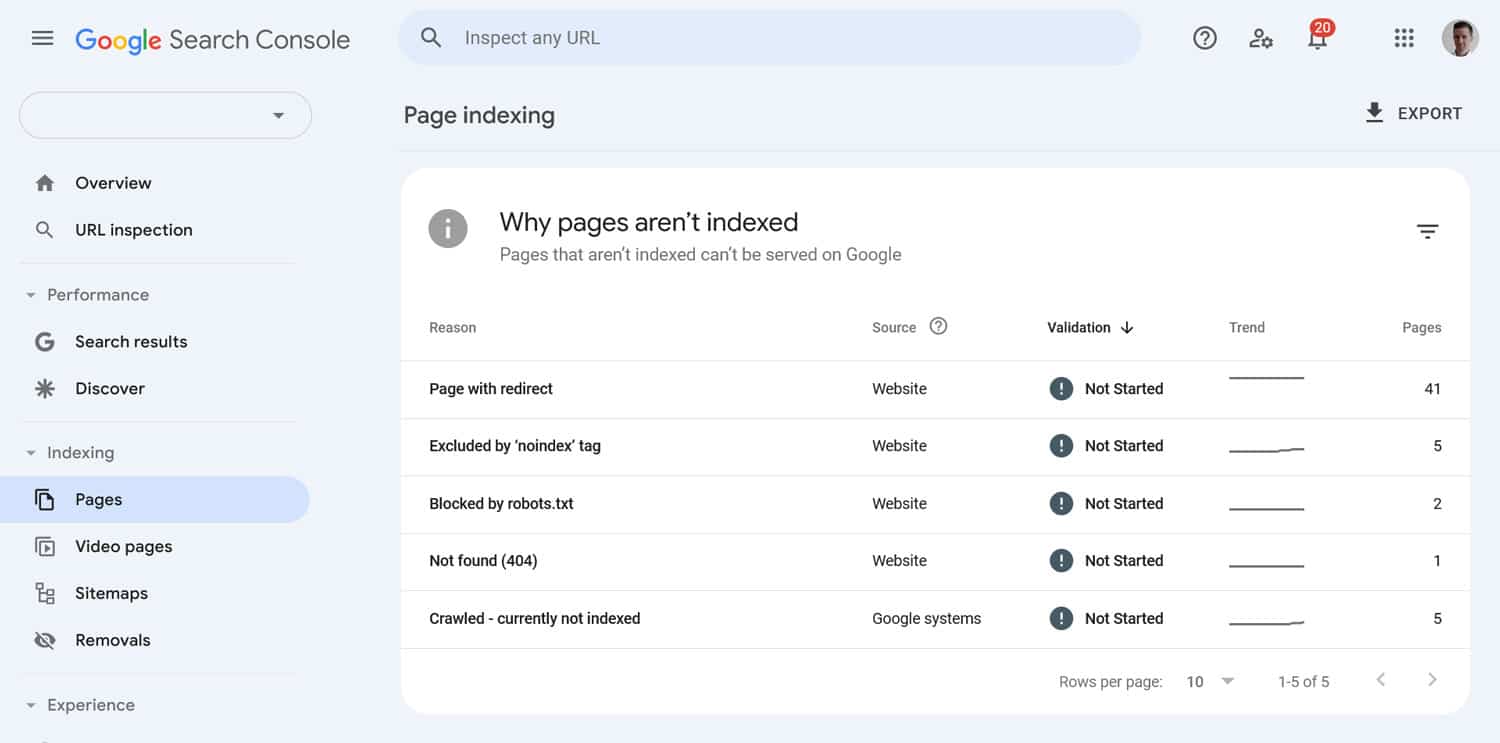
Aside from that, check the Pages report in Google Search Console. It will tell you about crawl errors and the reasons behind them.
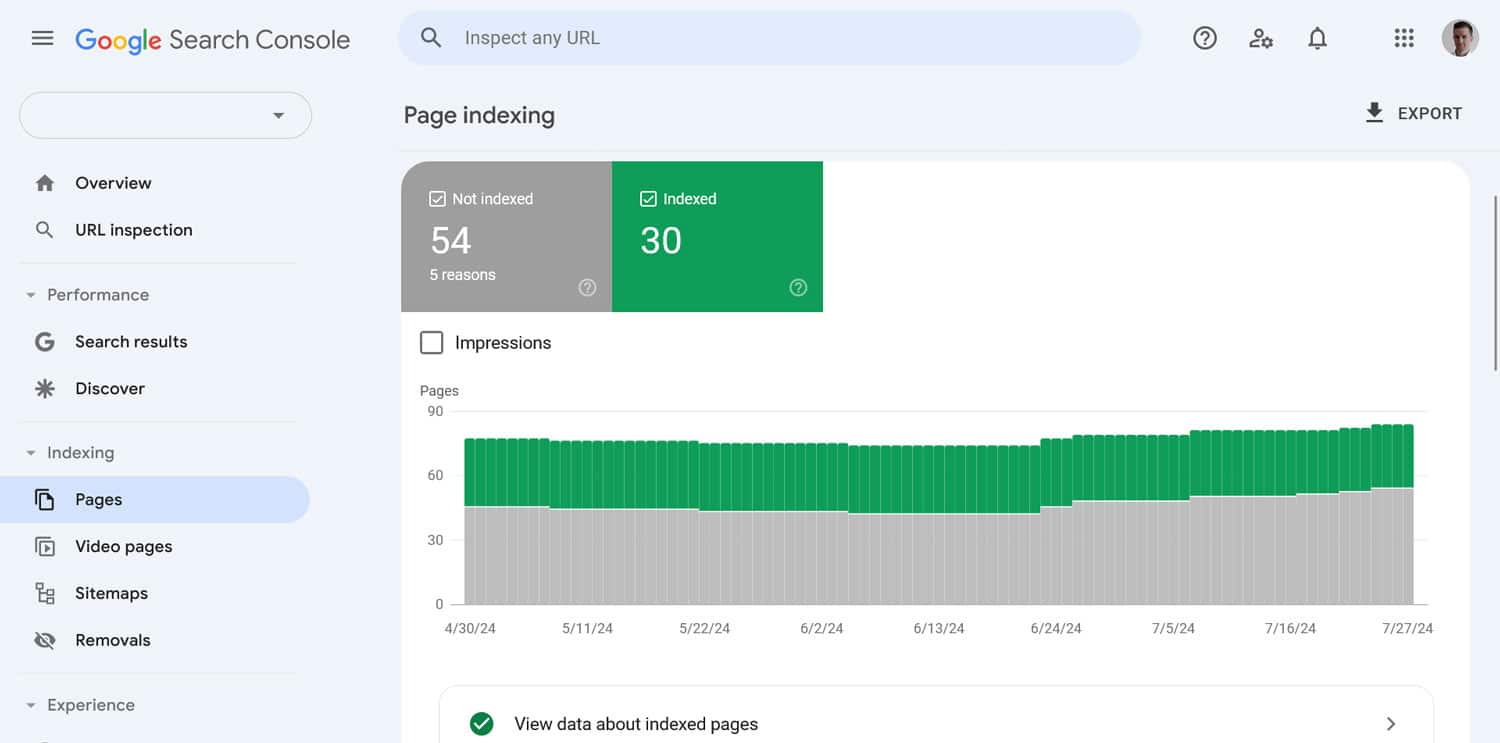
Plus, you can paste any page address at the top of the Search Console to find out its individual indexing status and manually request indexing.
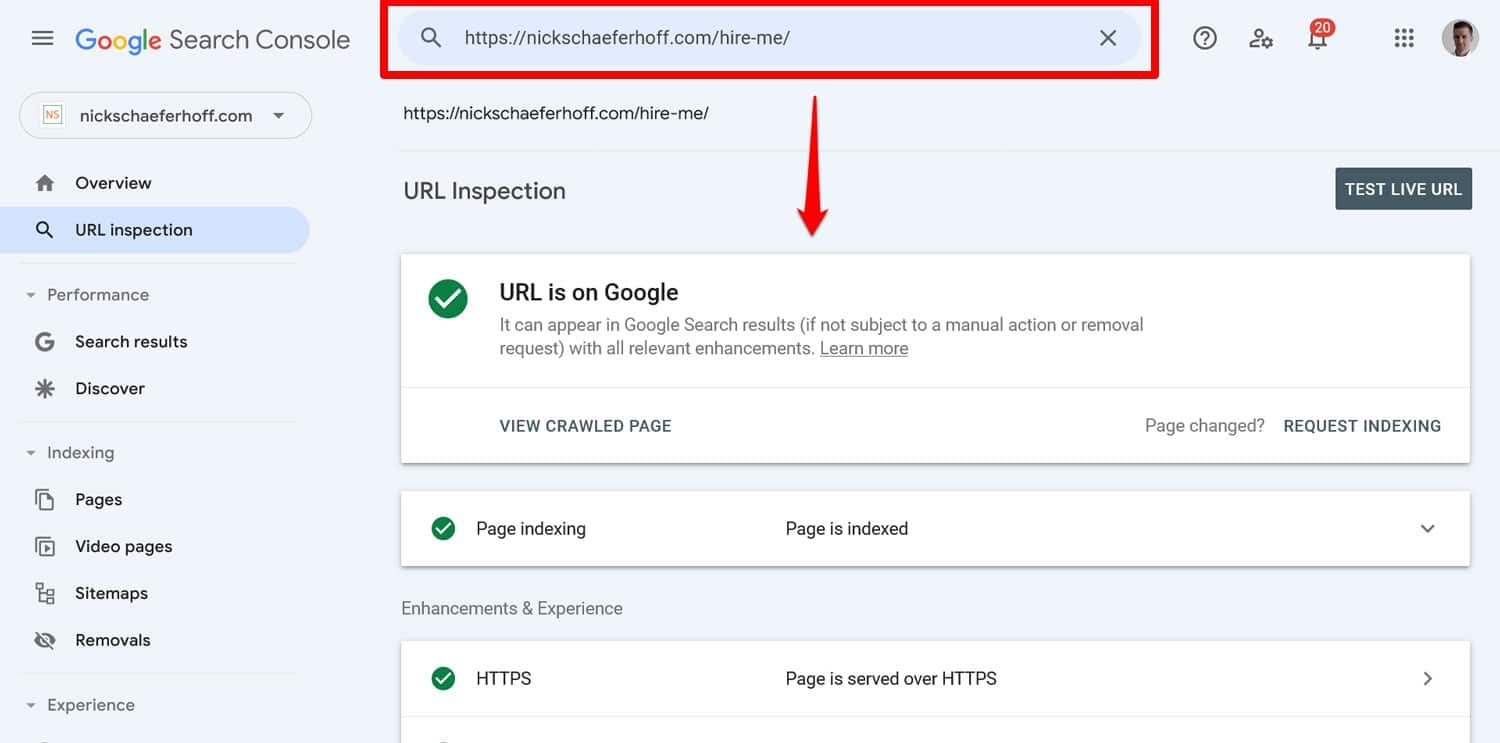
In case you find that search engines can’t index your site, first of all check the search engine visibility option under Settings > Reading in the WordPress dashboard.
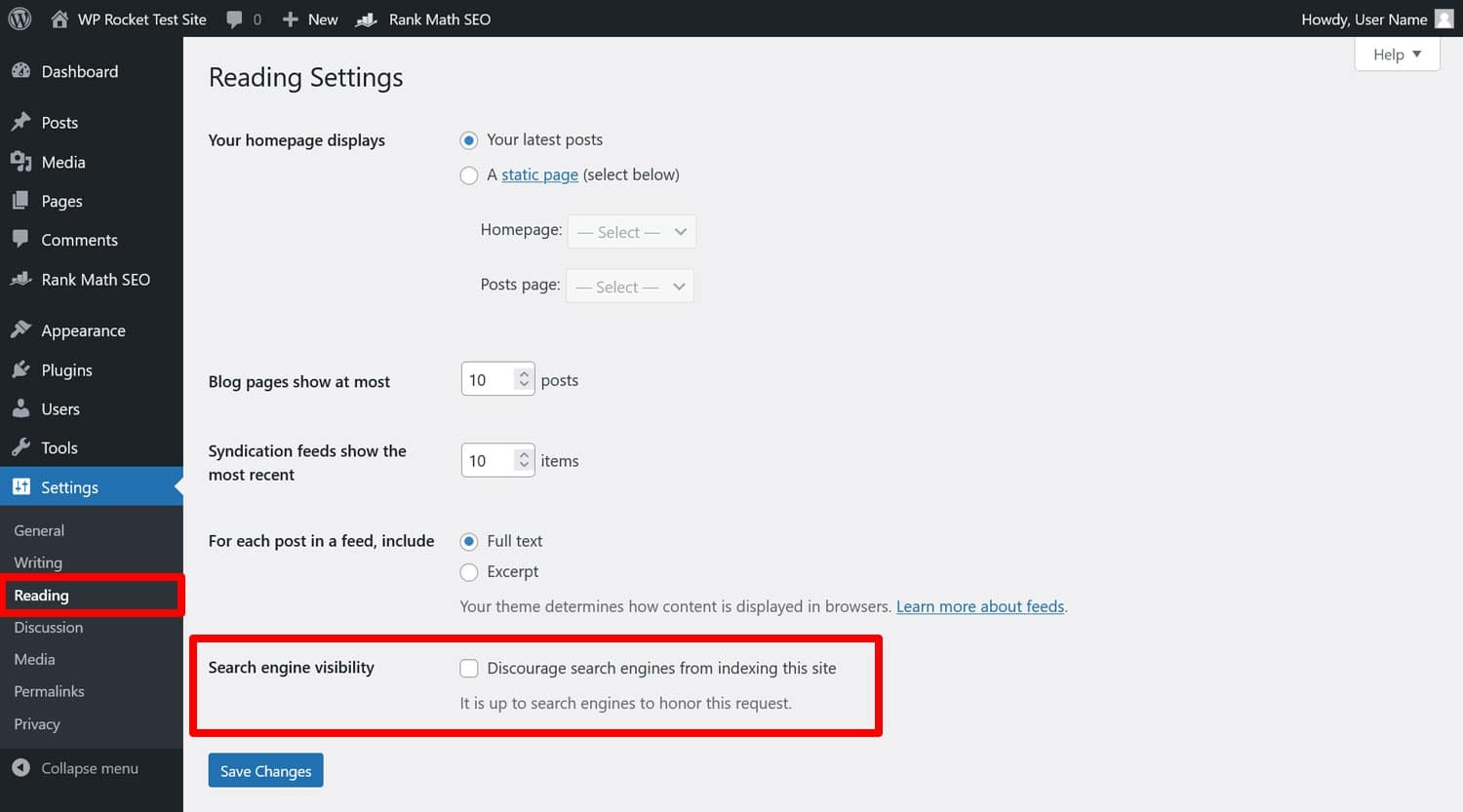
If the box that says “Discourage search engines from indexing this site” is checked, you have found the culprit. But crawl issues can also come from other factors that we will talk about, like robots.txt.
5. Use SSL/HTTPS
HTTPS/SSL is an encryption method that secures data transfer between visitors and your site. Google and other search engines reward sites that use it, making this part of technical SEO for your WordPress website.
You can see the SSL status of your website by looking for the padlock symbol in your browser bar.
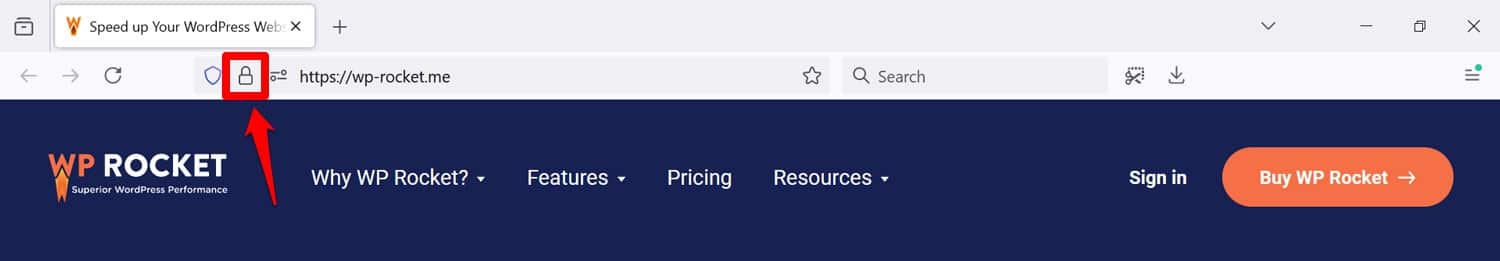
It also shows up in Google Search Console under Experience > HTTPS.
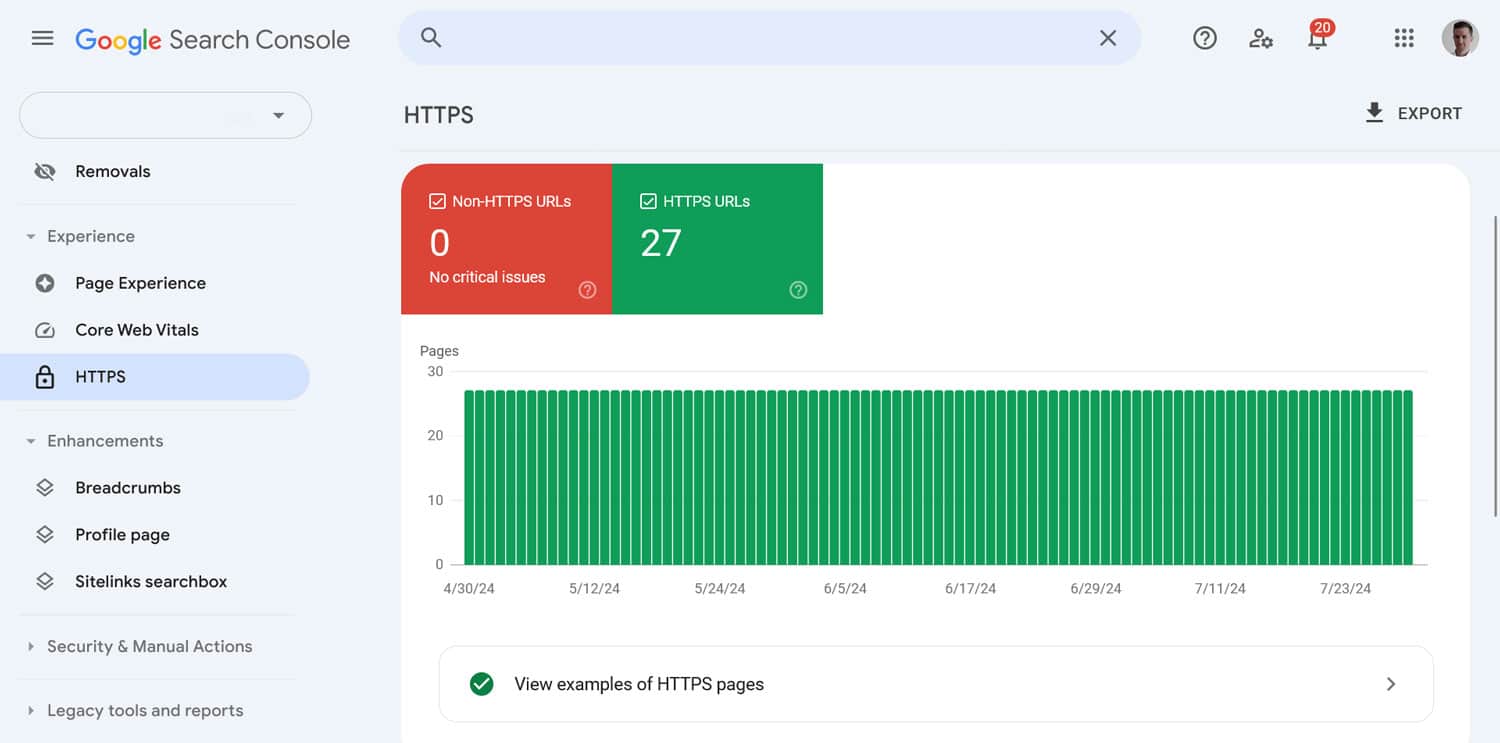
To implement HTTPS, you need to obtain and install an SSL certificate. Don’t worry if that sounds complicated; you can usually do it with a few clicks via your hosting provider. It might even be included by default. Plugins like Really Simple SSL make transferring WordPress website traffic to HTTPS easier.
6. Settle on a Singular Site Address
You can often access your site via multiple addresses:
While it’s clear to you that all these are the same website, Google treats them as four different sites. Your task is to make sure to use only one, otherwise, you might run into problems with duplicate content.
We already mentioned that it’s best if you use HTTPS. Whether you want to include www in your URL is up to you. After you’ve decided, check that the chosen version is in the WordPress settings under General and the “WordPress Address (URL)” and “Site Address (URL)” fields.
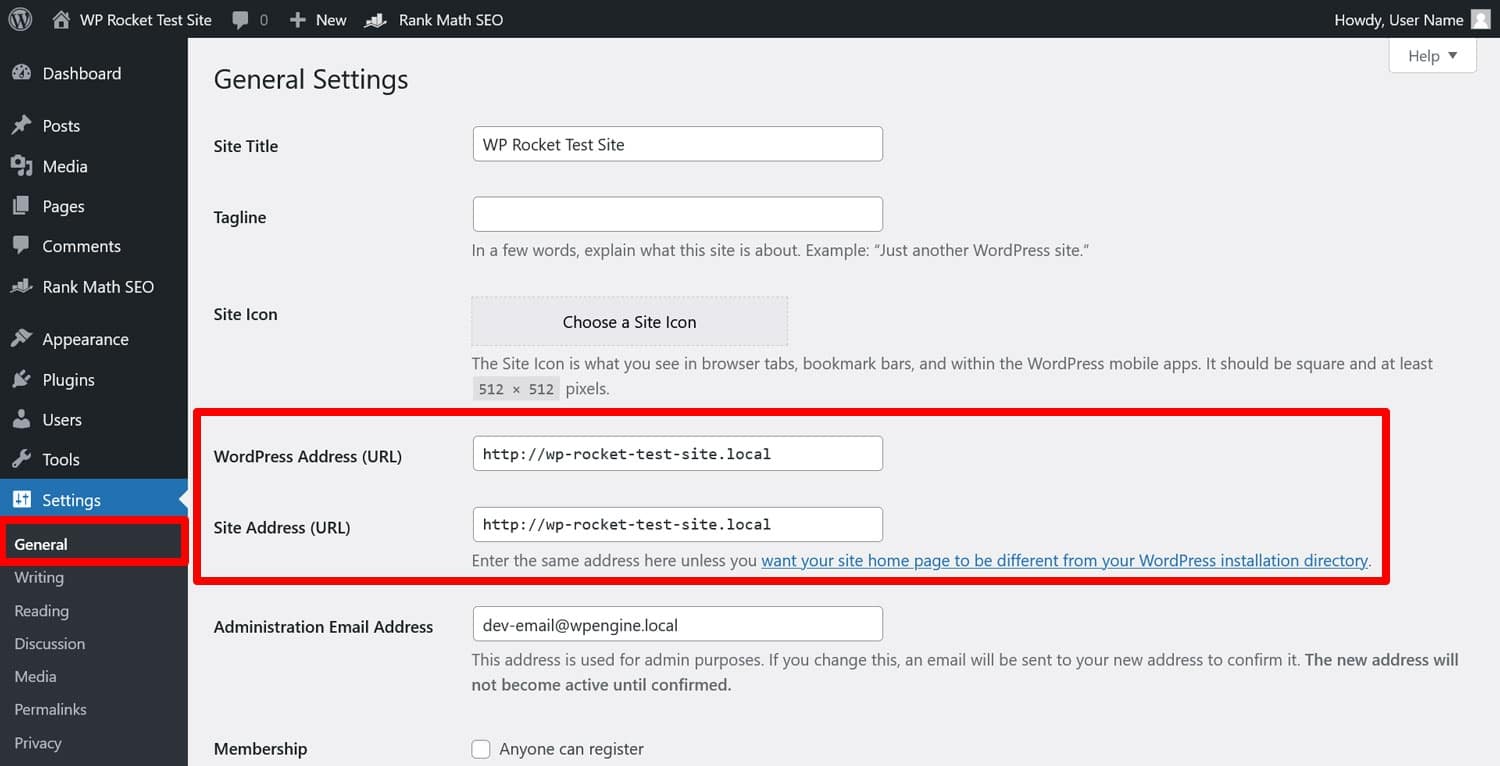
After that, point all other versions to the right address, too:
- Use Screaming Frog to crawl your site for URL deviations
- Set up redirects if necessary (more on that below)
- Point all internal links to the right address
- Set up canonical tags when duplicate content is unavoidable
7. Use an SEO-Friendly URL Structure
After settling on the main website address, now it’s time to deal with the rest of the URL structure. It needs to ensure website links are readable and descriptive. This helps visitors and search engines understand the content and hierarchy of your website.
Just compare these two examples:
- https://www.yoursite.com/p=123
- https://www.yoursite.com/best-coffee-makers
Which one is better? Exactly.
In WordPress, you can control URLs in two different places: Settings > Permalinks and the page and post editor.
The first option allows you to set the overall URL structure.
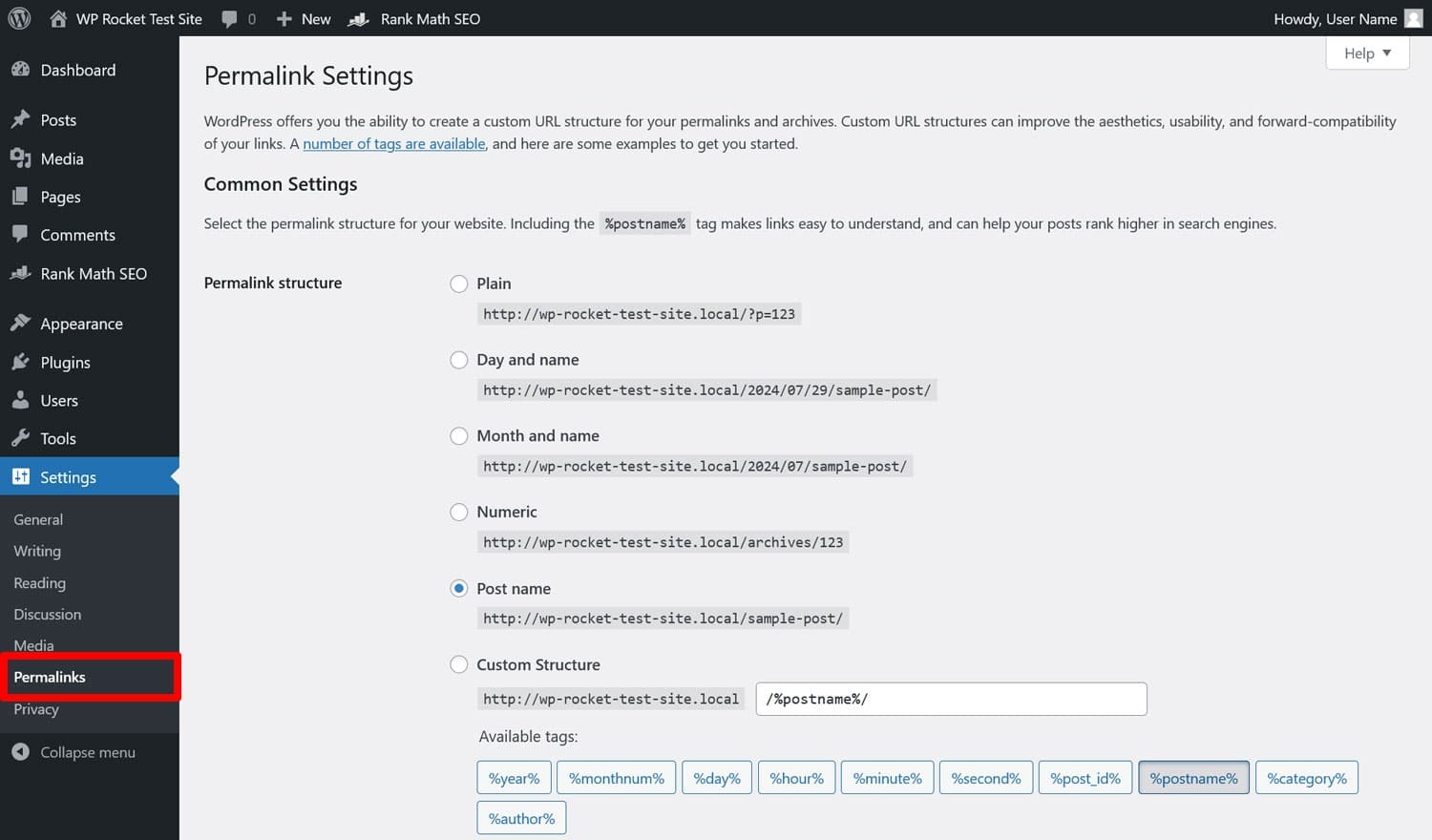
Choosing Post name is the most common option. You can also include categories in your URLs, however, avoid dates unless it makes sense, for example, for a news site.
Then, include meaningful slugs, which is the end part of the URL, in the WordPress editor. You do that in the sidebar.
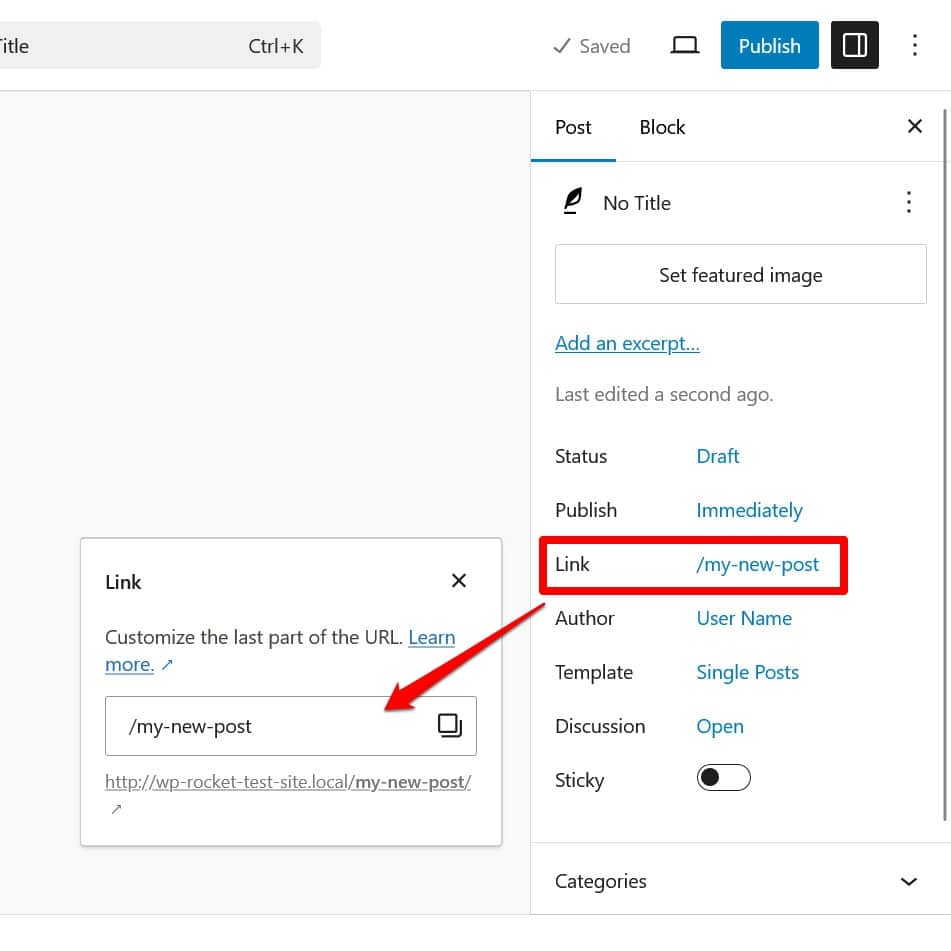
Keep your URLs short and descriptive, and include the main keyword. That’s pretty much it.
8. Find and Correct Broken Links
Broken links are those that lead to a 404 error page.
They can happen due to a typo but typically because a page no longer exists. Broken links frustrate users and negatively impact SEO.
How do you find them? First of all, they show up in Google Search Console under Pages when you choose to see non-indexed pages and scroll down for the reasons they are not in the index.
You can also use the aforementioned Screaming Frog or SEO tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs.
Once identified, fix broken links by setting up 301 redirects to move visitors and search engines to the correct or related content. A plugin like Redirection helps you do so. In addition, regularly check your site for links that go nowhere.
9. Examine Your Internal Linking Structure
Talking about links, using them to connect your content internally is another part of technical SEO. It improves user navigation and helps distribute link equity.
Something to look out for here are orphan pages—pages that don’t receive links from anywhere else on your site. It makes them hard for search engines to find. Rank Math has a great tutorial on how to find and fix orphan pages.
To avoid them in the first place, make sure to always link to relevant articles within your content. In addition, use anchor text that accurately describes the link target.
10. Ace On-Page SEO
On-page optimization means structuring your content so that it’s easy to understand.
The first step for that is to use headings correctly and in the right order. A page should only have one H1 tag implemented by your theme. Use H2 and H3 headings as necessary to create sections and subsections.
In addition, optimize your title tags and meta descriptions since they show up in search results.
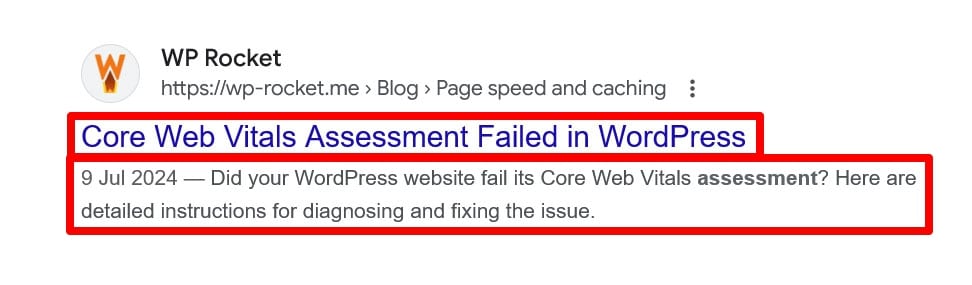
You can do this with an SEO plugin like Rank Math.
11. Optimize Images
Images are another important factor for page performance because they are data-heavy.
To optimize them, use them only as large as needed, compress them to reduce size, and use next-gen image formats that are naturally smaller.
You can control the image sizes WordPress automatically creates when uploading under Settings > Media.
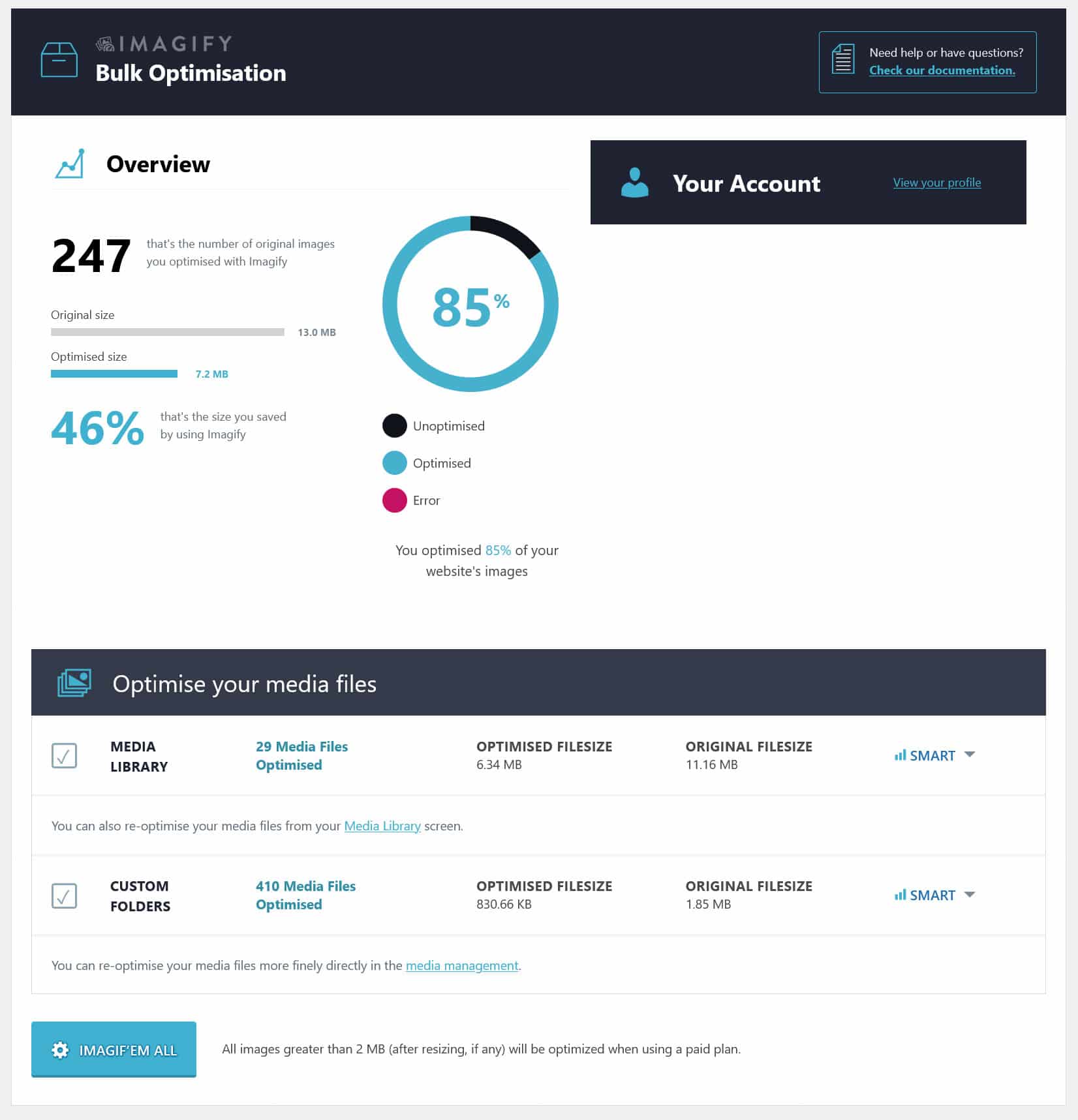
There are many tools to compress images before uploading them, but a more convenient way is to use Imagify. When installed on your WordPress site, it automatically compresses and resizes any image uploaded to your site without losing quality. It can also optimize visuals in bulk and convert them to modern image formats. It’s super easy to use, too.
Finally, be sure to include ALT text on all your images. This lets search engines know their content, is a good place for keywords and is important for accessibility.
12. Generate Sitemaps and Submit Them to Search Engines
Sitemaps are essentially lists of all the pages on your website and help search engines discover and index your content more effectively.
You can also submit them to webmaster tools like Google Search Console for that purpose.
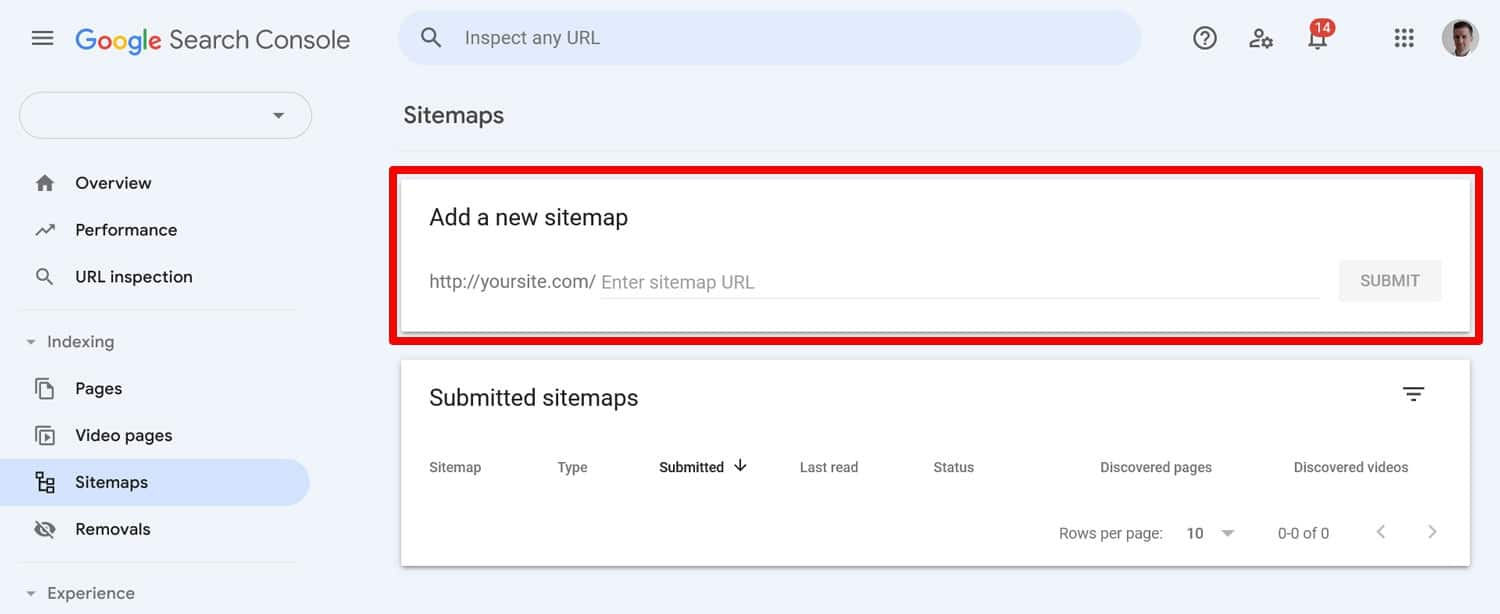
There are several ways to create sitemaps in WordPress. Many SEO plugins come with this function built-in. You can use a standalone plugin like XML Sitemap Generator.
13. Use Schema Markup
You’ve most likely seen Schema markup in action before. It’s responsible for search results with additional information like images, ratings, reviews, and event details.
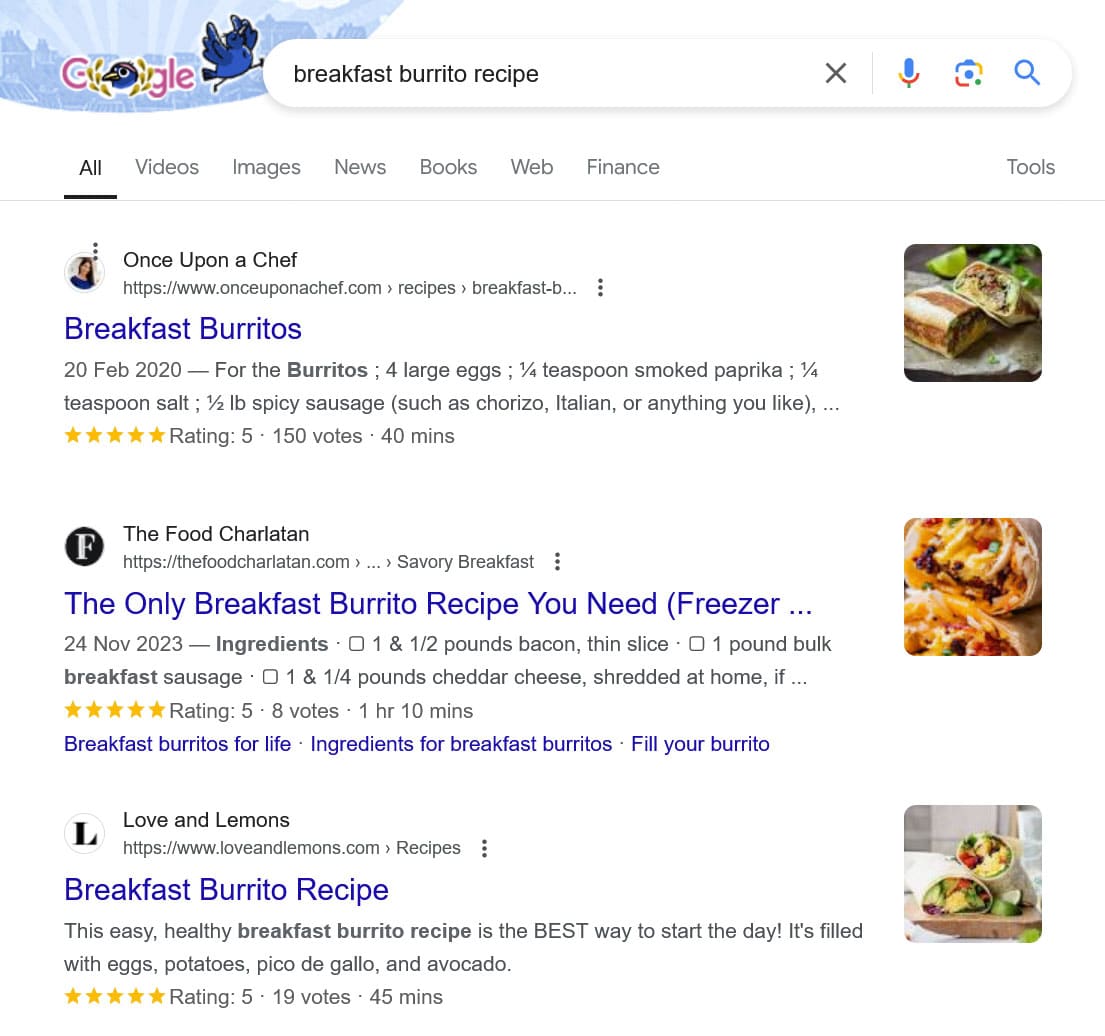
It helps improve click-through rates and you can do it for your site, too. Schema markup exists for recipes, reviews, events, FAQs, blog posts, multiple locations for local businesses, and more.
How can you add it to your site? Many popular SEO plugins can do it for you, or you can use a standalone solution like Schema.
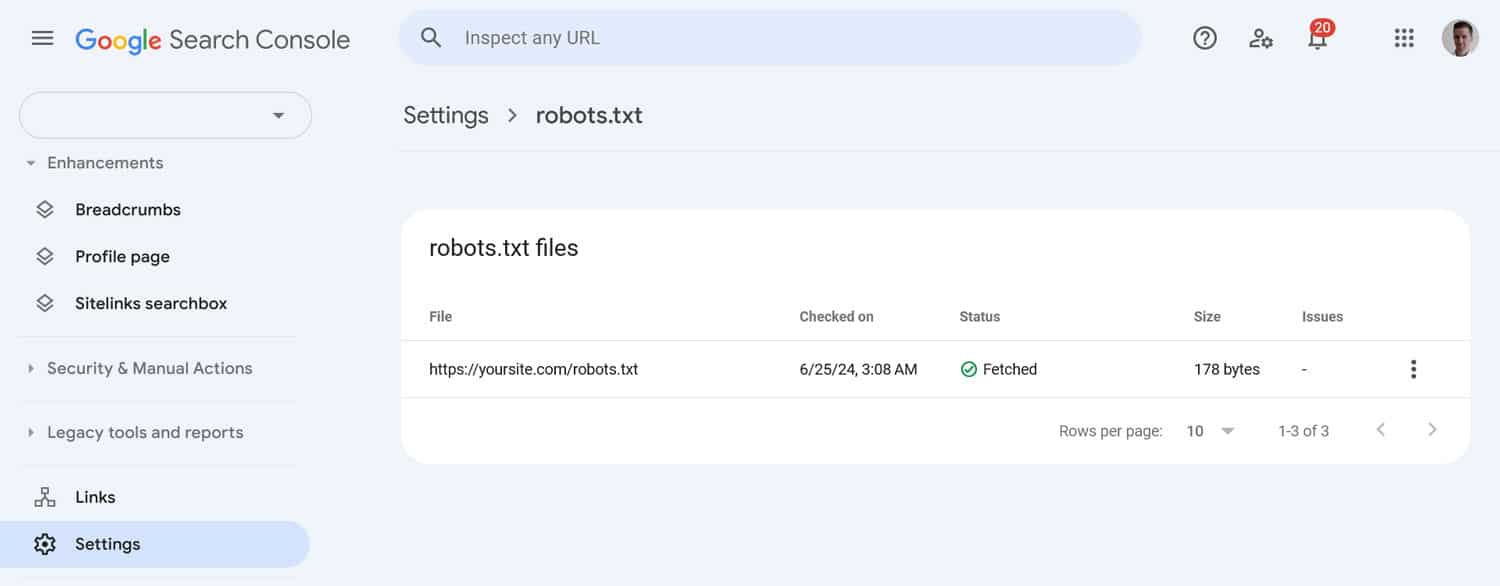
14. Optimize Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a powerful server file. It contains directives that tell search engine crawlers which content to crawl and which not. For example, the option in WordPress that tells search engines not to index your site works with an internal robots.txt file.
A misconfigured robots.txt file can be highly detrimental to your WordPress website’s technical SEO. Conversely, a well-configured file can help direct the crawl budget and even tell crawlers where your sitemap is.
Here’s what the content of a typical robots.txt looks like:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
In most cases, you should not have to deal with this file because WordPress automatically configures it well. But it’s important to be aware of its existence because, if you have problems with your site being indexed, it’s one of the things to check.
Google has a great write-up on robots.txt, and there is a report in Google Search Console.
Finally, there are a number of robots.txt generators out there, such as this one, which you can use to set rules for your file.
15. Protect Your Website From Malware
Malware can harm your site’s reputation, leading to deindexing from search. Therefore, keeping your WordPress site safe is definitely part of technical SEO. Regularly scan it with security plugins like Wordfence or Sucuri.
In addition, implement robust security measures such as regular updates, strong passwords, backups, and monitoring for any suspicious activity. Implementing a Web Application Firewall (WAF) can also add an extra layer of security.
16. Invest in Accessibility
You might wonder how accessibility is related to SEO. Well, there’s an accessibility indicator in Google’s PageSpeed Insights. Is that a convincing argument?
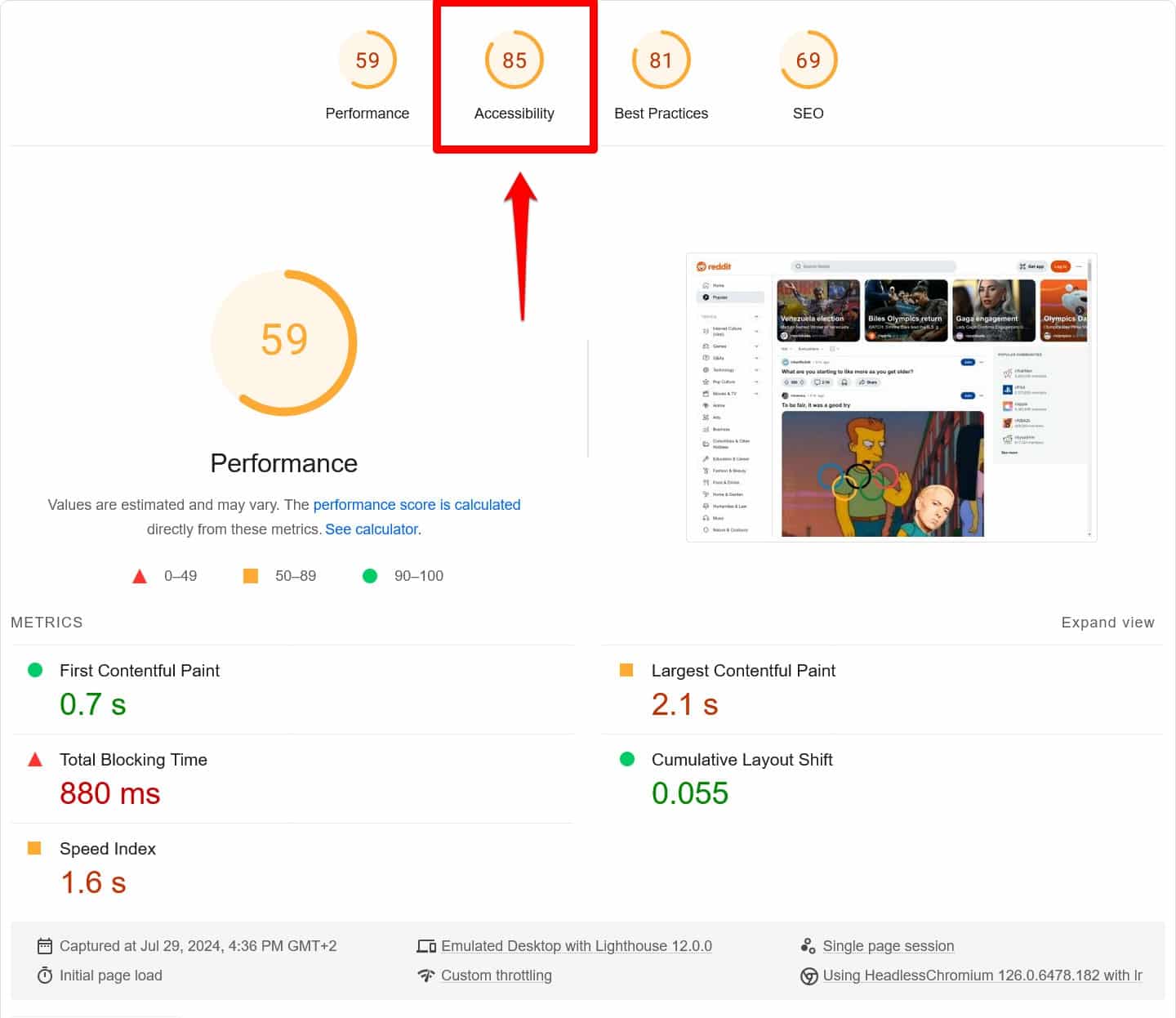
Google obviously cares about accessibility. And while it’s not a direct ranking factor, accessible websites tend to come with stronger user experience signals, which do factor into search positions. For that reason, just like for performance, PageSpeed Insights tells you how you could do better in this area.
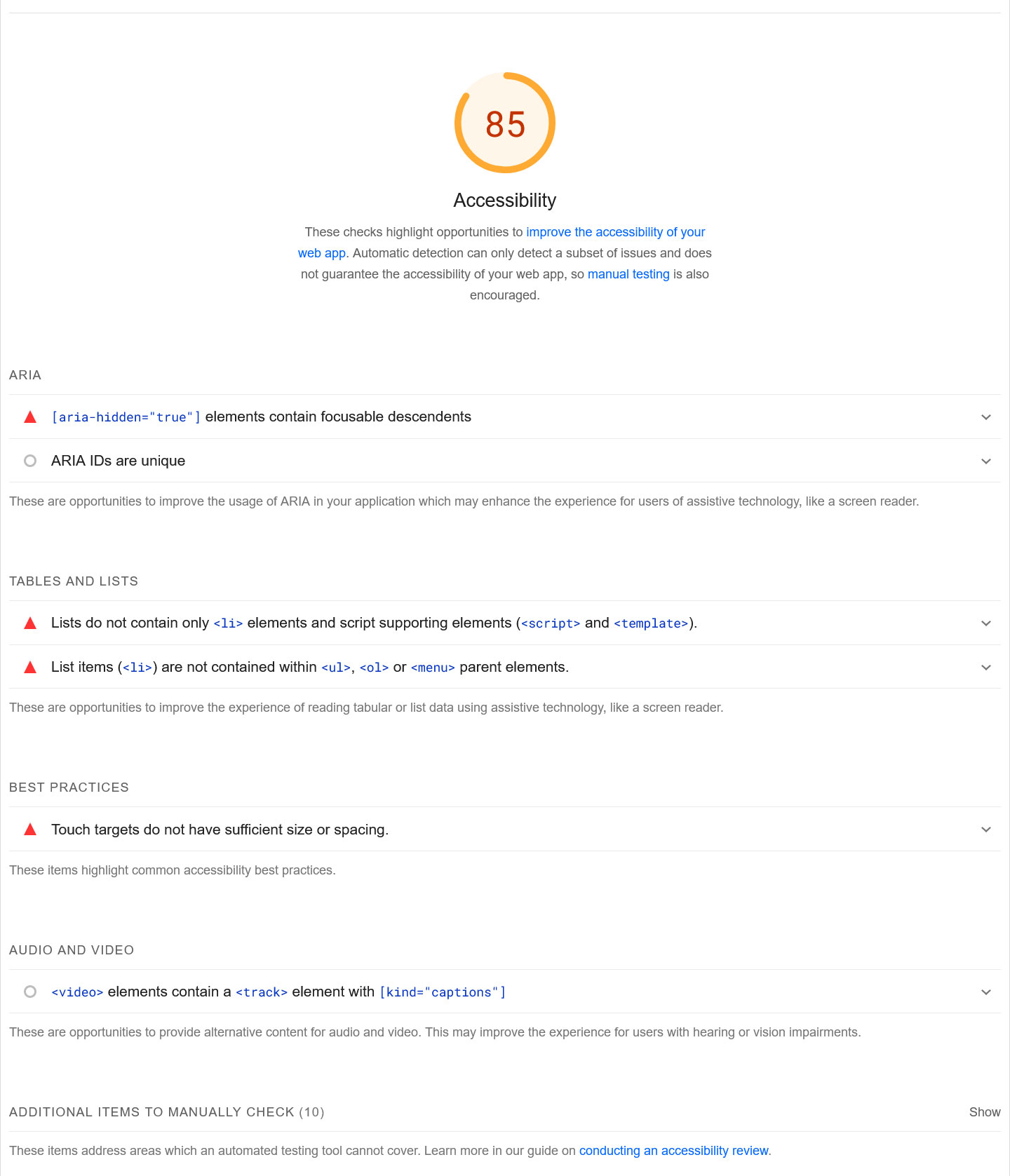
In addition, there is considerable overlap between technical SEO and making your website easier to use for people with disabilities. For example, ALT text for images and the proper use of headings matter for both.
Besides that, the most important factors are sufficient color contrast and working keyboard navigation. Check out the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) for the full list.
Take Control of Your WordPress Site’s Technical SEO
Technical SEO is the foundation for your WordPress site ranking performance. It makes sure your site is easy to browse and index for search engines, mobile-friendly, and loads fast.
By now, you’ve learned actionable ways to ensure your technical SEO is at the level it needs to be. Implementing them one by one puts your site in the best position to earn the search traffic it deserves.
If any of these steps seem daunting, don’t be afraid to get help. Particularly optimizing site performance can be challenging. If that’s the case, consider automating it via performance plugins like WP Rocket and Imagify.



