Table of Contents
Last update on
When it comes to decreasing your website’s load times, your DNS and how quickly it responds are often overlooked.
Without it, users would need to remember the long string of numbers of your IP to visit your website instead of a user-friendly address.
Since Google’s research indicates your website’s bounce rate can increase by 32% if it loads between one and three seconds, it’s essential to shave off as much time as possible from page load speeds.
Today, I’ll share more details on DNS testing and how you can run your DNS response time test to see if you can improve the performance of your DNS and website’s speed.
What is a DNS?
Domain Name Servers (DNSs) are like phone books for websites, linking them to their IP addresses. In turn, a DNS lookup is the process of finding the correct IP address for a given website URL.
Domain names such as “wp-rocket.me” require the assistance of DNS servers to translate the domain name into a numeric IP address so that users can access the right site.
How do DNS Servers Work?
Understanding how DNS servers work might help troubleshoot when you have DNS problems. For example, a number has a name and a number attached to it. The name is what people type into a browser to access a site, such as our website wp-rocket.me.
Numbers or IP addresses are associated with that domain name and indicate the location of the website on the internet. A DNS server’s job is to tie the name to the number.
When a website’s name is put into the browser, it queries the nearest DNS server for its IP address. When the DNS server delivers the IP address, the browser connects to the webpage, which shows on your screen. Unfortunately, end users are unaware of the necessary background processes to keep the system running.
If the DNS server is unavailable, the browser cannot get the website’s IP address and returns an error. Because it takes seconds for the news to spread, everyone knows the server is down.
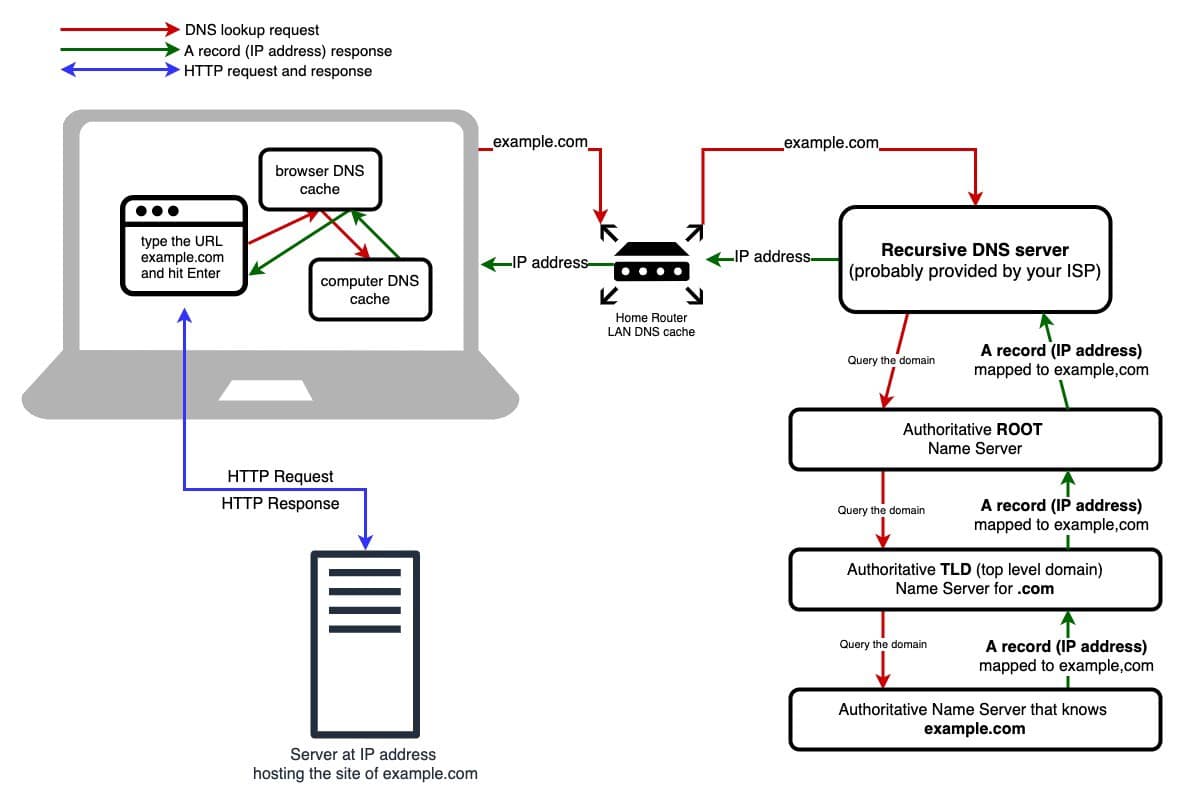
Here’s a quick step by step process of how it works once you type in the domain name you want to visit:
- Requesting website information.
- It contacts the recursive DNS servers
- It looks for the authoritative DNS servers, or it looks elsewhere
- Access the DNS record
- Returns the record to your computer to your browser
And entire DNS process takes only milliseconds to complete, and as a site owner, you want to reduce DNS lookup as much as possible.
Two Methods And Two Very Different Tests
The two methods are:
- Ping test
- Dig test
Site owners and developers commonly run ping tests to measure the average time for a site to load.
While these tests give helpful information, they are not always trustworthy.
Some servers consider pings to be unnecessary and do not respond to them. Unfortunately, when this occurs, you will be unable to generate data on how fast your site loads.
Ping tests also don’t always disclose how quickly your DNS responds and fetches the IP address needed to load a page.
This is when the BIND tool comes into play.
It may be used to execute a DIG (Domain Information Groper) command to get your actual DNS response time.
It comes with Mac and may be downloaded and installed on Windows.
Using dig to test DNS server response time
The DNS response time results show just one metric from your computer, and it is essential to conduct your tests from other locations to get more accurate findings. You may run further tests using Google’s Public DNS.
To run a DIG command and DNS response time test, go to your Applications folder on Mac and open the Terminal app.
For Windows, go to Start > Run, enter “cmd” (without the quotation marks) into the field, and press Enter on your keyboard. Then, click on Command Prompt to open it.
Next, type in the command in the link below, but don’t forget to replace “your-site.com” with your actual domain before pressing Enter on your keyboard:
time dig example.com
Furthermore, you must enter the command in the link below, but remember to change your site’s domain with your actual domain before pressing Enter.
In this case, we’re showing a result similar to the one shown below for the DNS response time test performed for Google. The real-time is recorded in minutes, then seconds, followed by a period and milliseconds during the test.
The query time is recorded to determine how long it takes for your computer to execute the command, whereas the real-time determines how long it takes for your computer to contact your site’s DNS.
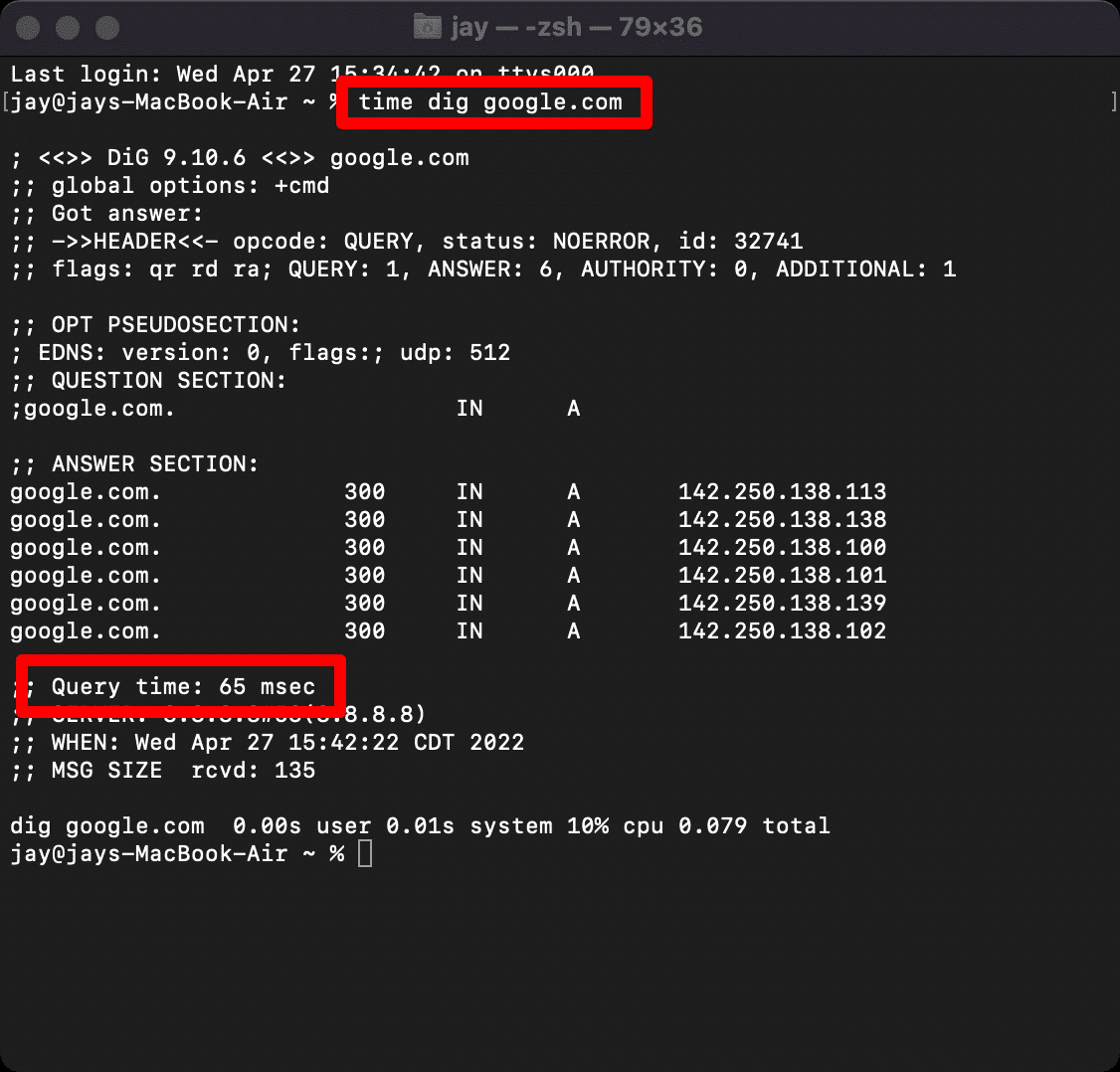
The results are identical to the previous commands, and you can get DNS response time by subtracting the real-time from the query time.
Digging Deeper into a DNS Response Time Test
The resulting DNS response time test shows only one metric from your computer. To get more accurate results, you must run tests from different locations.
You can use Google’s Public DNS, for example, to run more tests.
Go back to your Terminal app or Command Prompt and enter the following command:
Don’t forget to replace “your-site.com” with your actual site address.
The results are similar to the previous command, and you can subtract the real-time from the query time to get the DNS response time.
You know how to test DNS server response time using the DIG command, but how reliable are your results, exactly?
The Problem When You DIG for Results
While the BIND tool and DIG commands are helpful, there are some caveats.
Have No Fear, You’re (Probably) in the Clear
Lighting-fast DNS speeds are significant, but that’s not the only factor you should consider when trying to improve your site’s performance.
Many DNS options out there are sufficient. So unless you’re experiencing an alarmingly large DNS response time close to or much longer than a second for a small to medium-sized site, you’re probably in the clear.
Although, this isn’t a hard and fast rule. Each site is different. It’s up to you to decide what’s an appropriate DNS response time since it will vary based on the purpose of your website.
As Valuable as Your DNS’s Speed
How quickly your site’s DNS performs isn’t the only factor you should consider. What’s equally critical is that your DNS is secure and reliable, and your provider acts ethically, professionally, and takes your privacy seriously.
If security and privacy aren’t a priority for you, they should be since hackers can cause many issues for your site’s speed.
For example, they could inject scripts that add spam to your site that increases load times or redirect your domain to point to their spam, malware, or phishing website.

If your DNS isn’t reliable, it could be slow one minute, then fast another, and your visitors could get downright annoyed and decide to leave your site altogether.
Similarly, your hosting provider should also help you with any DNS issues courteously and quickly. Otherwise, you could struggle with your site’s speed for the long haul.
Possibly Skewed Results
The DIG command does a DNS lookup, but only from your computer or another DNS of your choosing.
Depending on how close your site’s DNS is to your computer or the DNS you used to run the test, you may not get accurate results for how your users experience your site’s speed.
If you’re located near your DNS and server, you’re going to get much faster response times than a user from the other side of the world and vice versa.
Not every one of your users will likely visit your site from your location. Unfortunately, that means some of your site’s visitors may experience higher or lower response times depending on how far they are away from your site’s DNS and server.
Getting results from only one or two different DNS locations isn’t going to provide an accurate overview of the average DNS response time for your site.
Ideally, Google’s Public DNS would be located on the opposite side of the world from your computer’s location, and your site’s DNS would be located near either you or the public DNS.
In that case, your results wouldn’t be as limited.
But, this may not be the case.
Fortunately, there are automated tools you can use to get more accurate results when you test DNS server response time.
Tools to Test DNS Server Response Time
Both of the tools listed here are free to use and do not need any software installation. They are both dependable and secure, and they provide complete reports after each DNS response time test.
DNSPerf
The DNSPerf tool performs real-time checks from over 30 locations to provide a comprehensive picture of how well your DNS performs worldwide.
Each location is marked with the amount of time it took your DNS to reply, and bad timings are highlighted in yellow as a warning or in red to indicate significant speed difficulties.
The results are given in list form and on a map for clarity.
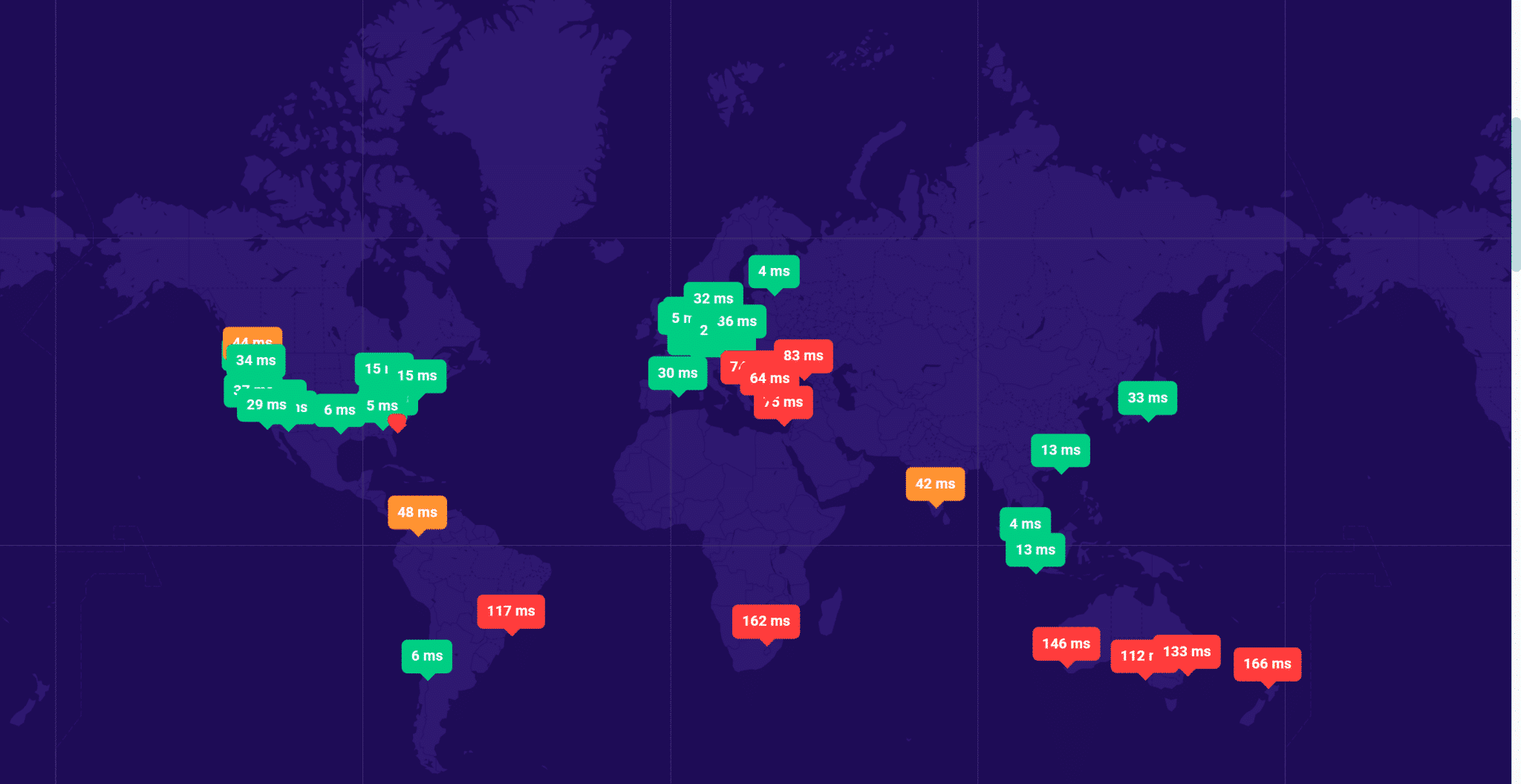
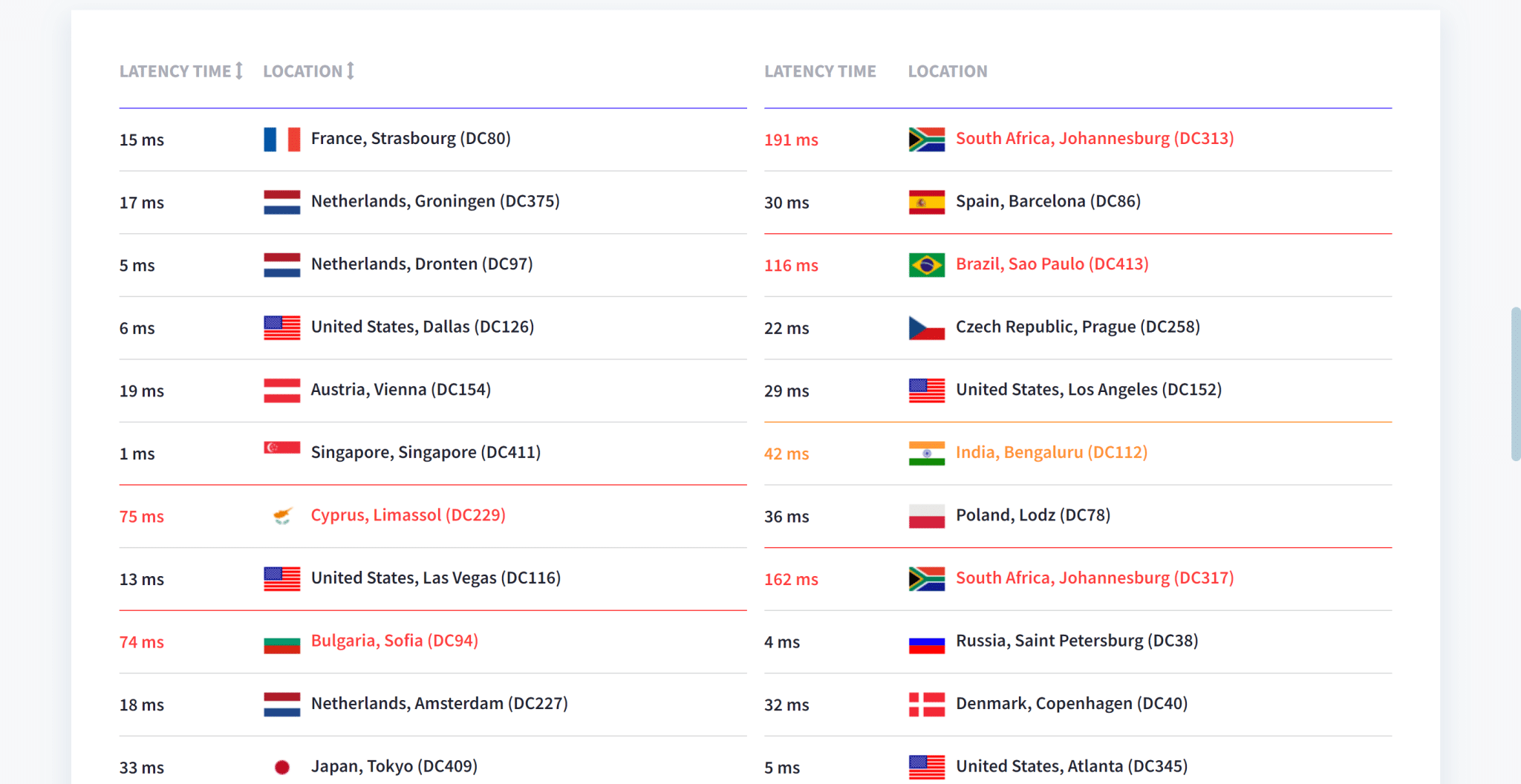
Probably the best tool, and that looks great. But you can also scroll down and see the list of locations and response times:
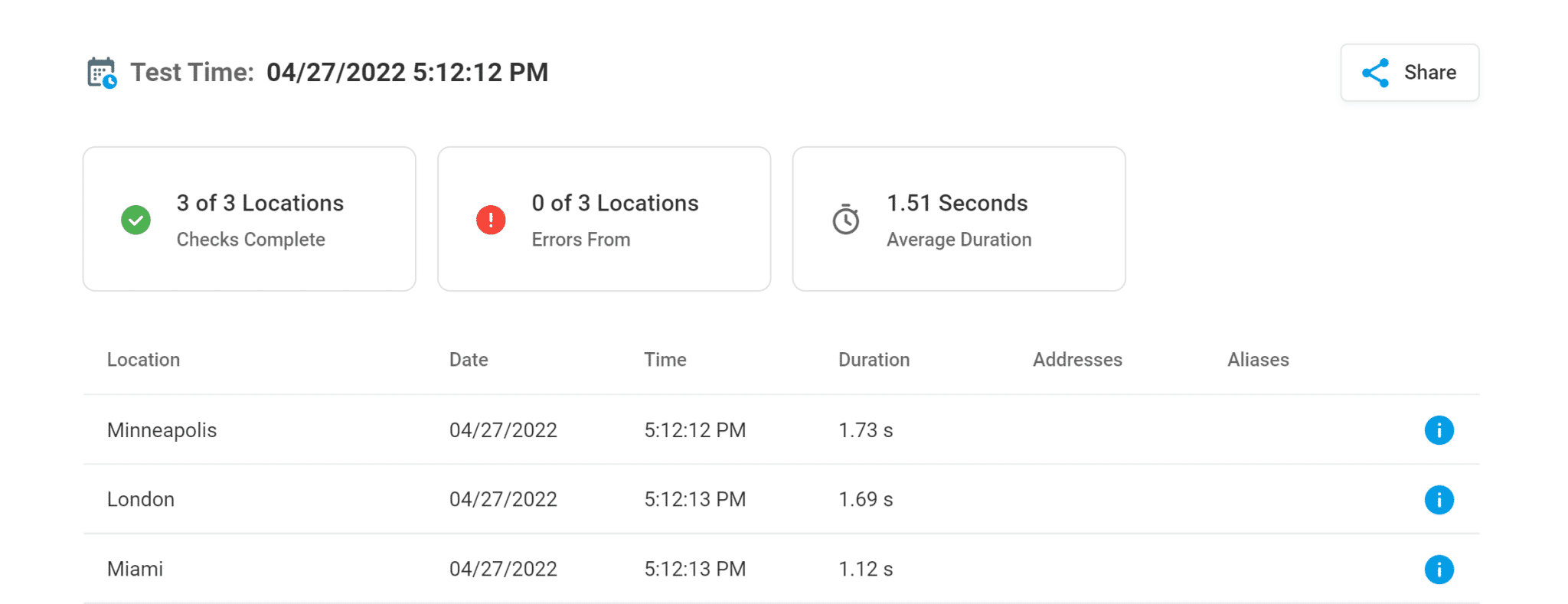
DotCom-Tools
The DNS lookup test from DotCom-Tools asks root servers to obtain DNS lookup records that specify the path followed to acquire authoritative DNS server data. The IP addresses associated with the requested DNS record are returned by the DNS server. If IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are available, the DNS trace test will attempt to resolve them automatically.
The ability to choose the countries you want to test a page’s load and response time on is an excellent option if you’re testing a specific area for your business. The time it takes to obtain a response from each node along the path, and the responses given from each node are included in the test results.
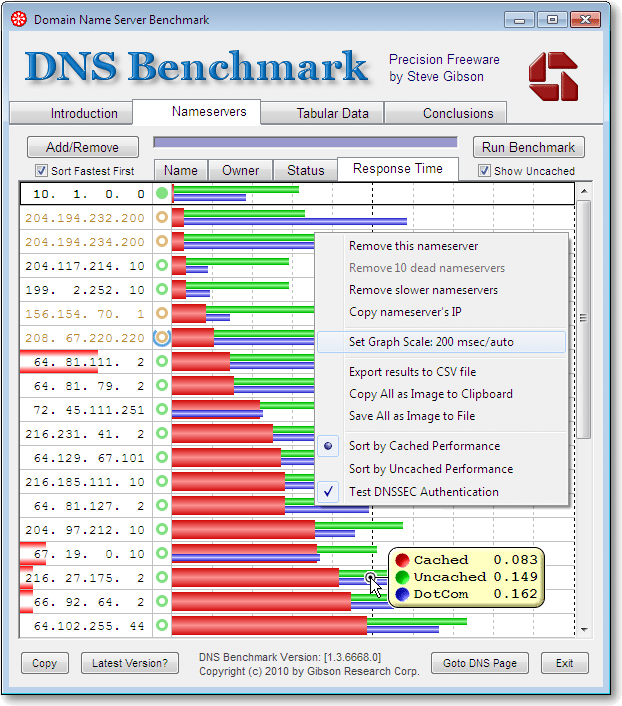
GRC DNS Benchmark
GRC DNS Benchmark is a standalone tool provided for Windows and Linux to test local and remote name servers. You can compare the performance and reliability of up to 200 DNS resolvers with Cached/uncached/dotcom lookup. View the findings in tabular or graphical form or export the results to CSV format.
Wrapping Up
In certain circumstances, shaving milliseconds – or seconds – off your DNS response time might drastically reduce your site’s load times. It will also aid in the improvement of the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) grade, which is one of the Core Web Vitals.
A DNS response time test using the DIG command can help you identify whether your DNS is operating properly or whether it needs to be improved.
In any case, you’ll know if your DNS speed is enough.
Do you test the response time of DNS servers? Have you considered your DNS while reviewing the overall performance of your site?