Table of Contents
Last update on
Do you want a fast-loading website? Of course you do! This guide to website speed optimization explains how to optimize a website step by step, using simple, proven techniques. We cover the most common mistakes to avoid, the best website speed best practices to follow, the right tools to use, and practical checklists to help you stay on track.
You’ll also learn how to maintain website performance over time, so your site stays fast as you publish new content and add new features!
A faster site means happier visitors, better engagement, and a higher chance of ranking well on Google. Ready to improve website load times and boost your website performance i?
| TL;DR Website speed optimization is mostly about removing what slows your site down and keeping the essentials fast. The biggest wins usually come from caching, image optimization, CSS/JavaScript cleanup, plus smart loading for above-the-fold content. Track the right KPIs to improve website load times: monitor Core Web Vitals, fully loaded time, page weight, and HTTP requests to measure website performance optimization and see if your website speed strategy is working. |
Key Takeaways
✅ The biggest website performance mistakes are slow hosting, no caching or CDN, heavy images and videos, too many third-party scripts, and poor above the fold prioritization.
✅ Using the right tools saves time: GTmetrix to measure speed, WP Rocket to apply performance best practices, RocketCDN to speed up global delivery, and Imagify to optimize images.
✅ Test your site in real conditions: check several URLs, multi devices, different locations, and mobile connections (4G).
✅ Maintain performance over time: retest regularly, optimize every new upload, and review plugins and scripts to prevent slowdowns.
What’s Website Speed Optimization?
Website speed optimization refers to all the performance techniques used to create a fast-loading website. It is a comprehensive strategy that improves user experience, increases revenue, and even boosts SEO! Google rewards fast websites in its ranking algorithm, so it’s essential to have a whole strategy when it comes to optimizing your site.
Website performance optimization should be seen as a global issue, not only as how fast as text and images appear on a page. It goes beyond what users see and includes what happens behind the scenes, such as how your server, files, and resources work together to deliver your content.
Common website speed optimization techniques include:
- Using fast and reliable hosting
- Optimizing images and videos
- Using caching and a CDN
- Optimizing JavaScript and CSS so pages render faster

All these elements work together. If one part is slow, the whole website feels slow. That’s why website performance optimization requires a complete approach to truly improve website load times and build a fast loading website for every visitor.
To make this easier to understand, think about website speed like common questions you can ask yourself:
👉 About images:
Do I really need to load a very large image for a small mobile screen?
Could this image be smaller or compressed without losing quality?
👉 About code (JavaScript and CSS):
Does all my code need to load at the same time, or some scripts can wait until the main content is visible?
👉 About what users see first:
What does my visitor need to see immediately when the page opens?
Is the content below the fold really important right away? (Probably not).
👉 About performance in general:
Am I helping my site load faster for real users, especially on mobile and slow connections? Is my hosting powerful enough? Where are my visitors coming from?
This simple way of thinking is at the heart of how to speed up a website. Website performance optimization is also about choosing what to optimize first, so users get a faster experience.
Does it look a little bit overwhelming? Don’t worry! In the next sections, we will explore each technique in more detail and show you how to apply them step by step.
But first, let’s go over the culprits behind a slow site.
What Affects Website Load Times the Most?
The main factors that affect website load time are usually poor hosting, unoptimized JavaScript, missing caching, and large, unoptimized images. As shown in the graph below, page weight is mainly made up of images and JavaScript. In general, any efforts towards JavaScript and image optimization are a good start to reduce your overall page weight and improve loading speed.
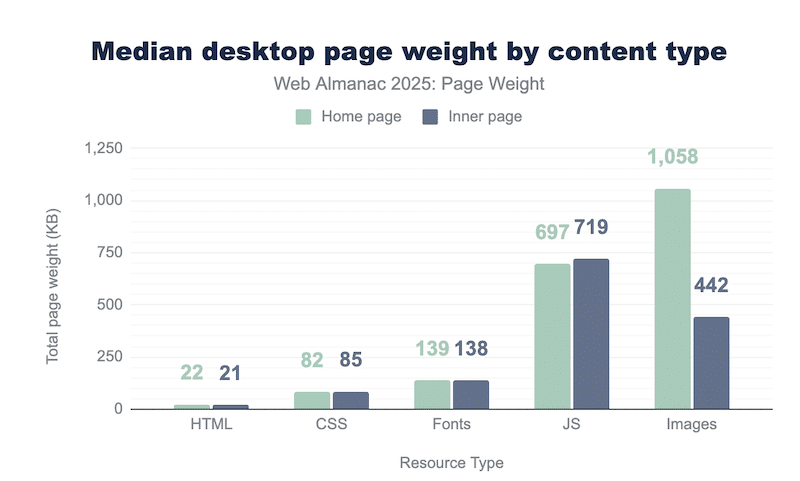
However, those reasons are for generic scenarios. The best way to find out what really slows down your site is to conduct a performance test.
How to Measure Website Speed and Performance
The easiest way to measure your website speed and performance is to use a Lighthouse-powered tool like GTmetrix. It analyzes your site and displays key performance indicators (KPIs), including Core Web Vitals, fully loaded time, page weight, and the number of requests. Here’s what a performance report looks like:
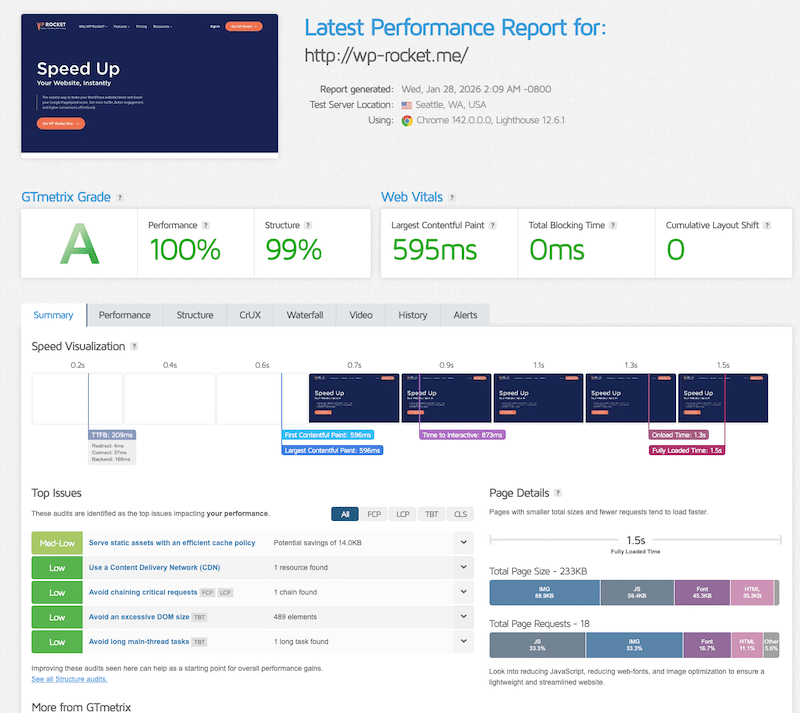
| 💡 Hint: The best approach is to run a test before and after applying optimization techniques to clearly understand their impact. |
Below are the main metrics you should measure to build a fast-loading website:
Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP and CLS)
Core Web Vitals are one of the most effective ways to measure user experience. Google uses them as ranking signals, which makes them critical for both SEO and performance.
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): how fast the main content appears.
Example: A slow-loading hero image means a poor LCP.
- INP (Interaction to Next Paint): how fast your site responds to user actions.
Example: A delayed button click means poor INP.
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): how stable the page is while loading.
Example: Moving text or buttons due to an ad pop-up may increase CLS.
Fully Loaded Time
It shows how long it takes your entire page to load. If your page takes more than 3 seconds to load, visitors may leave before engaging with your content.
Time to First Byte (TTFB)
It measures how quickly your server starts sending data to the browser. A slow TTFB often means your hosting or server setup needs improvement.
Page Weight
It represents the total size of your page, including images, JavaScript, and videos. Heavy media usually explains slow-loading pages.
HTTP Requests
It shows how many files your browser must download to display the page. More requests usually mean slower load times.
| 💡 Hint: When you want to measure website speed and performance, remember to: ✅ Test on mobile due to slower network conditions (4G or throttled connections). ✅ Use different locations from your servers to see how international visitors are experiencing performance on a larger scale. ✅ Test several URLs, not just your homepage, to identify bottlenecks on your entire site. |
18 Website Performance Optimization Best Practices
To make website speed optimization easier, we grouped our 18 best practices into clear categories: hosting, content delivery, code, media, and mobile performance. Follow these tips to improve website performance, reduce loading times, and create a fast-loading website that delivers a better experience for every visitor.
📁 Hosting and Server Optimizations
1. Choose a Fast and Reliable Hosting Provider
Your hosting provider is the foundation of your website. A slow server will delay every page to load, even if your site is optimized.
👉 Example: A website on a low-cost shared host loads in 6 seconds, while the same site on a high-performance and dedicated server loads in 2 seconds.
🛠️ Best solution: A quality hosting provider such as one.com, Kinsta, Flywheel, or Bluehost.
2. Optimize Server Configuration for Speed
Modern server technologies such as updated PHP, HTTP/2 or HTTP/3, and compression (GZIP or Brotli) help your server send data faster to the browser. These settings reduce server response time and allow multiple files to load more efficiently at the same time.
🛠️ Best solutions:
- Enable HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 directly to your server configuration (Apache or NGINX).
- Activate compression (GZIP or Brotli) at the server level to reduce file size before sending data to visitors. This can be done manually or via plugins like WP Rocket, the easiest and most powerful performance plugin for WordPress that applies 80% of the performance best practice upon its activation (including GZIP compression).
| 🚀 Performance hint: WP Rocket does not only apply GZIP. It’s also the simplest performance plugin because caching, CSS/JS minification, and lazy rendering are activated right upon activation. The intuitive interface also allows you to enable powerful features, such as, removing unused CSS, loading JavaScript deferred, and delaying JavaScript execution in a few clicks – features which are helpful for the rest of our checklist. |
📁 CMS and Website Environment Optimizations
3. Use a Lightweight Theme or Framework
Heavy themes with animations and effects increase page size and slow down page loading, while a lightweight theme or framework increases your chance of running a fast website.
👉 Example: A simple theme or template loads in 2 seconds, while a complex theme can take 5 seconds with complex JS issues.
🛠️ Best solutions: Performance-focused themes or templates and fast CMS like WordPress or Wix.
4. Limit the Number of Plugins and Extensions
Each plugin adds extra code and requests. Keeping only what you need helps reduce load time.
👉 Example: A site with 40 plugins may load slower than one with only 12 essential plugins.
🛠️ Best solutions: Use QueryMonitor to identify slow plugins and run tests on tools like GTmetrix or PageSpeed Insights every time you add a new plugin or when you make an update.
5. Keep Your CMS and Software Up to Date
Updates include performance improvements and bug fixes.
👉 Example: After updating the CMS and plugins, pages load faster, and some compatibility errors disappear.
🛠️ Best solution: Use your CMS update manager, such as WPUmbrella for WordPress.
6. Optimize Third-Party Scripts and External Tools
Third-party scripts are external tools added to your website, such as analytics, chat widgets, video players, social media buttons, or advertising trackers. Each of these scripts sends requests to other servers and must load before your page becomes fully usable, which can slow the load time of your content.
👉 Example: A homepage with a YouTube video, a chat widget, and several tracking tools forces the browser to load many external scripts before showing the main content. Removing unused analytics scripts and replacing autoplay videos with click-to-play videos can greatly improve homepage speed.
🛠️ Best solution: Use Google Tag Manager to control when and how scripts load without editing your site’s core code. If your site is made with WordPress, you can use WP Rocket to delay or control third-party scripts.
📁 Content Delivery and Data Distribution
7. Implement Caching for Faster Page Delivery
Caching stores ready-to-use pages so they do not need to be rebuilt for each visitor.
👉 Example: A product page loads instantly for repeat visitors.
🛠️ Best solutions: Cloudflare provides browser caching and edge caching for faster page delivery. If you are a WordPress user, then you can use WP Rocket‘s automatic caching features.
8. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN delivers your website files from the closest point of presence to each visitor, rather than from a single central server. This reduces distance, improves loading speed, and creates a faster experience for users around the world.
👉 Example: A visitor in Europe loads images from a nearby server instead of the origin server located in the US.
🛠️ Best solutions: Cloudflare or RocketCDN, the simplest CDN that does all the technical setup for you. If you use WordPress, All you need to do is activate the plugin to deliver assets faster across the global network.
📁 Critical Content Prioritization (Above the Fold Optimization)
9. Use Prefetch, Preconnect, and Prerender Techniques
Prefetch tells the browser to download resources that will be needed soon, while preconnect prepares the connection to external servers in advance, so files load faster when requested.
👉 Example: When a visitor clicks from your homepage to a product page, the browser has already prepared the font and image files, so the next page appears almost instantly.
🛠️ Best solutions: Add prefetch and preconnect tags directly in your HTML header. For WordPress users, use WP Rocket’s preload feature.
10. Enable Lazy Loading for Images and Videos
Images at the bottom of a long page should only load when the visitor scrolls down, rather than loading all at once when the page opens.
🛠️ Best solutions: Add the lazy loading attribute directly to your media files, for example: <img src=”image.jpg” loading=”lazy”>. For WordPress users, use the WP Rocket LazyLoad feature to enable lazy loading for images, CSS Backgrounds, and videos.
11. Prioritize Critical Images with Fetch Priority
Hero images and main visuals should load first because they’re usually the most critical content on your page. By giving them higher priority, you ensure that important content appears quickly and improves the perceived loading speed of your website.
👉 Example: The main banner at the top of the page appears instantly, while gallery images further down the page load later as the user scrolls.
🛠️ Best solutions: You can assign high priority directly in your image code, for example: <img src=”hero.jpg” fetchpriority=”high”>. For WordPress users, WP Rocket applies the Fetch Priority feature upon its activation.
📁 JavaScript and CSS Optimization
12. Remove Unused CSS
Unused code increases page weight and slows down rendering. You should always clean and trim unnecessary code on your pages.
👉 Example: A contact page no longer loads slider scripts meant for the homepage.
🛠️ Best solutions: You can use an online tool like CSS Optimizer, or if you are a WordPress user, WP Rocket’s “Remove Unused CSS” feature will do the job.
13. Load JavaScript with Defer or Async
Deferring JavaScript allows content to load before scripts run. JavaScript scripts control interactive features on a website, such as buttons, forms, animations, and pop-ups. Deferring JavaScript means these scripts run after the main content is visible, so users can see and use the page faster.
👉 Example: Text and images appear immediately instead of waiting for scripts to load.
🛠️ Best solutions: You can use the Defer and Async attribute directly on your code or use WP Rocket’s JavaScript defer option if you manage a WordPress site.
14. Delay Non-Critical JavaScript Execution
Some JavaScript scripts are not needed immediately when the page opens, such as chat tools, analytics, or social media widgets. Delaying them allows your main content to load first and improves perceived speed.
👉 Example: A chat tool loads only after the user scrolls.
🛠️ Best solutions: Delay scripts using a simple trigger in your code, for example:
<script src=”chat-tool.js” defer></script> This means the script only loads after the page content is visible or after the user interacts with the page.
You can also use WP Rocket’s Delay JavaScript Execution feature.
📁 Media Optimization
15. Compress Media Without Losing Visual Quality
Image compression reduces file size while keeping images clear and sharp for users. Large images take longer to download, slowing down your pages, especially on mobile devices. By compressing your images, you send lighter files to the browser without changing how they look on screen, which helps improve website load times and overall performance.
👉 Example: An image goes from 2 MB to 200 KB with no visible quality loss, making the page load much faster.
🛠️ Best solutions: You can compress images manually with tools like Photoshop, but it has a steep learning curve and takes time. For WordPress users, Imagify is the easiest image optimization plugin. It automatically applies bulk compression using saving you hours of manual work. Thanks to its Smart compression, you get a smaller file size and a perfect image quality.
16. Use Next Generation Image Formats
Next-generation image formats such as WebP and AVIF are designed to be much smaller than traditional formats like JPEG and PNG while keeping excellent visual quality. Smaller image files load faster, use less bandwidth, and help create a fast-loading website for all users.
👉 Example: A JPG image can be about 45% smaller just by converting it to WebP, with no noticeable difference in quality.
🛠️ Best solutions: You can use online converters such as CloudConvert to convert images to WebP or AVIF. If you’re a WordPress user, Imagify lets you convert images to WebP and AVIF with a single click from the dashboard, making the process simple and automatic.
📁 Mobile Performance Optimization
17. Enable Mobile Specific Caching
Mobile users often browse slower connections and less powerful devices than desktop users. Mobile-specific caching stores optimized versions of your pages for smartphones and tablets, so they load faster without rebuilding the page on every visit. This helps improve website load times and creates a smoother experience for mobile visitors.
👉 Example: A mobile visitor sees the page instantly, rather than waiting several seconds for it to load over a 4G connection.
🛠️ Best solutions: Use a CDN or a server-side caching solution, such as Cloudflare, to cache mobile pages and serve them quickly to mobile visitors. For WordPress users, WP Rocket mobile caching creates separate cached versions of pages for mobile devices.
18. Serve Responsive Images for Different Screen Sizes
Responsive images adapt to device size, preventing large desktop images from loading on phones.
👉 Example: Your banner on a mobile would be 800px and not 2500px like on desktop.
🛠️ Best solutions: Use default image tools like Preview (Mac) or advanced tools such as Photoshop and Canva to create several image sizes. Then, you can use the srcset attribute to serve responsive images, allowing the browser to choose the best image size based on the user’s screen and device resolution.
Website Speed Best Practices Summary
In a hurry? This table shows the key website speed best practices and the easiest ways to implement them using simple tools and methods. Here’s how to speed up a site:
| Website speed best practices | Best solutions for a fast-loading website |
| Choose a fast and reliable hosting provider | Compare hosting performance and test your site with GTmetrix before and after switching hosts |
| Optimize server configuration for speed | Ask your hosting provider to enable HTTP/2 or HTTP/3, compression, and server caching |
| Use a lightweight theme or framework | Choose performance-focused themes and test demo pages with GTmetrix before installing |
| Limit the number of plugins and extensions | Test each new plugin with GTmetrix and remove those that slow down your site |
| Keep your CMS and software up to date | Use your CMS update manager and retest performance after major updates |
| Optimize third-party scripts and external tools | Manage and delay scripts with Google Tag Manager or WP Rocket and remove unused tools |
| Implement caching for faster page delivery | Use Cloudflare for any website or WP Rocket automatic caching for WordPress |
| Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Use Cloudflare or RocketCDN and test loading speed from different locations |
| Use prefetch and preconnect techniques | Add resource hints in your HTML header or use WP Rocket preload features |
| Enable lazy loading for images and videos | Use loading=”lazy” in your code or WP Rocket LazyLoad feature |
| Prioritize critical images with fetch priority | Add fetchpriority=”high” to hero images or use WP Rocket Fetch Priority feature |
| Remove unused CSS | Use online CSS tools or WP Rocket’s Remove Unused CSS feature |
| Load JavaScript with defer or async | Add defer or async attributes in your code or enable the option in WP Rocket |
| Delay non-critical JavaScript execution | Delay scripts with simple code triggers or WP Rocket Delay JavaScript Execution feature |
| Compress media without losing visual quality | Use tools like Imagify and compare before/after results in GTmetrix |
| Use next-generation image formats (WebP, AVIF) | Convert images with CloudConvert or Imagify and measure page weight reduction |
| Enable mobile-specific caching | Use Cloudflare mobile caching or WP Rocket mobile caching for WordPress |
| Serve responsive images for different screen sizes | Resize images with Photoshop or Canva before uploading and use the srcset attribute |
8 Common Website Speed Optimization Mistakes
Most slow websites are caused by simple issues like low-quality hosting, large images, unoptimized code, and not using caching. Let’s go over the 8 most common website speed optimization mistakes so you can avoid them.
1. Using a Low-quality Hosting
Your hosting provider is the foundation of your website. If your hosting server is slow or overloaded, your website will take longer to respond to every request.
👉 Example: Your homepage has a large hero banner and several images. If your hosting server is slow, even a simple page will take several seconds to load because the server cannot deliver the files quickly enough.
2. Not Caching Your Website
Caching stores a ready-to-use version of your website pages, so they do not need to be rebuilt every time someone visits your site. Without caching, your server must process each request for every visitor. This includes loading images, running code, and generating the page from the database. This makes your website much slower.
👉 Example: You have a product page with images, text, and a testimonial video. If caching is not enabled, your website has to rebuild the entire page every time a new visitor arrives. This causes longer loading times.
3. Not Using a CDN
A CDN, or Content Delivery Network, stores copies of your website files on servers located around the world. When someone visits your site, the files are delivered from the server closest to their location. Without a CDN, all visitors must load your website from the origin server, regardless of their location.
👉 Example: If your website is hosted in the United States but a visitor opens it from Paris, every image, script, and video has to travel a long distance before it appears on the screen. This increases loading time and can cause delays, especially for large images or banners.
4. Including Unnecessary JavaScript and CSS files
Unoptimized code means your website loads files that are too large or unnecessary. This usually includes unused CSS and JavaScript files.
👉 Example: Your homepage might load code for sliders, animations, or forms that aren’t even visible on this page. All these extra files increase load time and delay when the page becomes usable.
5. Serving Unoptimized Images
Images and videos are often the heaviest elements on a page. Problems happen when images are too large for their display area or are not compressed properly. Using formats like JPEG and PNG instead of WebP or AVIF also increases file size.
👉 Example: A banner image uploaded at full camera resolution for the homepage can be several megabytes in size, especially in PNG format and not using a next-gen format. This alone can slow down your page by several seconds; image optimization is essential to improve website performance.
6. Overusing Third-Party Scripts and Fonts
Too many third-party scripts and external fonts can slow down your website because each one adds extra requests and increases loading time.
👉 Example: Your homepage that uses several tracking tools, social media widgets, chat features, and multiple Google Fonts must load all these resources before the main content appears. This can delay page display and make the website feel slow for visitors.
7. Using Too Large Videos
Videos can quickly slow down a website if they are hosted directly on the server or loaded immediately when the page opens.
👉 Example:
A homepage with an autoplay testimonial video in MP4 format may load much more slowly than expected, especially on mobile devices or slow connections.
8. Not Prioritizing Important Content First
Your website should load the most important content first, especially what users see immediately when the page opens. This includes your main banner, headline, and key images. Lazy loading delays images and videos that aren’t visible right away, while optimizing critical image delivery ensures the main visual elements load as quickly as possible.
👉Example: If your homepage loads a gallery and footer images before the hero banner and call to action, visitors will see a blank or jumping screen for several seconds.
To conclude on the mistakes, we asked a web performance expert what the #1 mistake he sees on websites. Ozgar from WPFixFast shared the following insight:
“One of the most common mistakes I see when it comes to web performance is using large background images for the LCP element and lazy loading them. Instead, use a regular <img> tag with fetchpriority=”high” and avoid loading=”lazy” for above-the-fold images so the main content loads as fast as possible.”
This advice highlights the importance of prioritizing the elements that matter most to users. By loading your main content first and avoiding lazy loading on above-the-fold images, you can significantly improve your Largest Contentful Paint and deliver a much faster experience for your visitors.
Bonus: Common Website Speed Optimization Mistakes Checklist
In a hurry? Make sure you don’t make these mistakes and instead follow website speed best practices.
| Common Website Speed Optimization Mistakes | Website Speed Best Practices |
| ❌ Using low-quality hosting | ✔ Choose fast and reliable hosting and combine it with WP Rocket caching for faster server response |
| ❌ Not using caching | ✔ Enable page and browser caching with WP Rocket to serve ready-to-use pages to visitors |
| ❌ Not using a CDN | ✔ Use RocketCDN to deliver your website files from global servers closer to your visitors |
| ❌ Including unnecessary JavaScript and CSS | ✔ Minify and remove unused CSS and JavaScript using WP Rocket optimization features |
| ❌ Serving unoptimized images | ✔ Compress images and convert them to next-gen formats like WebP or AVIF using Imagify |
| ❌ Overusing of third-party scripts and fonts | ✔ Limit external scripts and delay non-essential scripts with WP Rocket to improve loading speed |
| ❌ Using too large videos | ✔ Host videos on video platforms and lazy load them with WP Rocket to reduce initial load time |
| ❌ Not prioritizing important content first | ✔ Prioritize above the fold content and use lazy loading so key elements appear first |
But enough with the theoretical tips, let’s go over a real case study that will show how website speed optimization techniques impact performance in real conditions and how much improvement you can expect with the right tools.
Real Case Study: How to Easily Improve Load Times and Performance
We’ve explored the most common mistakes and the best practices to improve website load times. We’ve seen that caching, CDN usage, JavaScript and CSS optimization, image optimization, and the choice of CMS and theme can strongly impact performance.
But do those best practices work in real life? Which recommendations have the biggest impact on performance?
If you use WordPress, many of these website speed best practices can be implemented easily with WP Rocket.
Let’s look at real data and see how WP Rocket can help to easily improve load times and performance.
Test Setup
To keep this test simple and realistic, we used a basic business website built with Astra and with the following structure:
- A homepage with a hero banner
- A “Our Services” section
- Testimonials
- A call to action
It looks like this, for reference:
- Server location: France
- Test location: USA
- Device: Mobile (iPhone 15)
- Testing tool: GTmetrix
What We Measure
We focus on two main areas which are:
Performance KPIs
These mobile performance metrics help us understand overall website speed and user experience:
- Overall performance grade
- Core Web Vitals (LCP and CLS). Note: We are not testing INP because it’s field data and our test site doesn’t have enough traffic on it.
- Fully loaded time
- Page weight
Audit and optimization insights
We also analyze what issues GTmetrix detects and which recommendations can fix them.
Step 1: Measuring the Current Situation (No Optimization)
First, we test the website without any optimization in place. This shows us how fast the site is in its default state. The goal is to understand the baseline performance and identify the main issues slowing down the site.
Let’s start with the audit on GTmetrix:
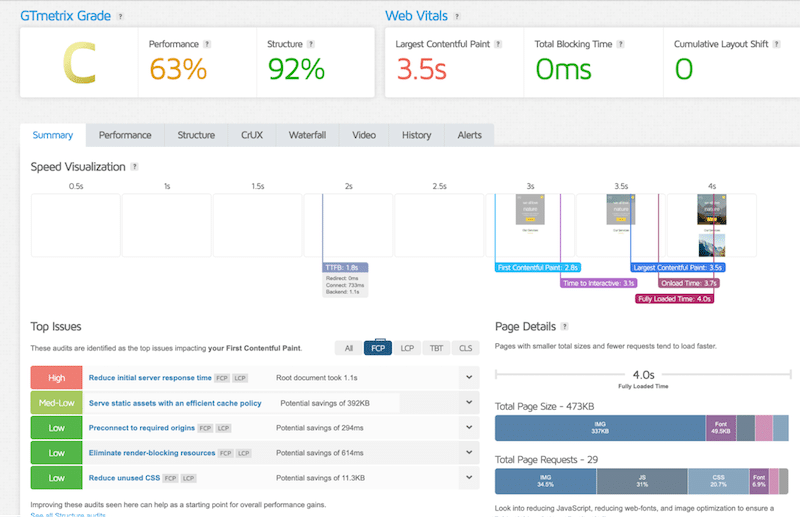
KPIs:
- Overall performance grade on mobile: C (63/100)
- Core Web Vitals (LCP and CLS): 3.5s and 0
- Fully loaded time: 4.0s
- Page weight: 472 KB
Audits and recommendations:
To improve website performance, GTmetrix recommends to reduce initial server response time (caching helps), implement caching, use preconnect, eliminate render-blocking resources (JS optimization) and reduce unused CSS.
Step 2: Applying Recommendations to Boost Performance
Next, we apply website speed optimization best practices based on GTmetrix recommendations, using WP Rocket.
Upon activation, the plugin automatically enables page and browser caching to reduce initial server response time and applies preconnect to speed up connections to external services.
And in just one click from the WordPress WP Rocket’s dashboard, you can:
- Defer JavaScript and load scripts after the main content to remove render blocking resources:
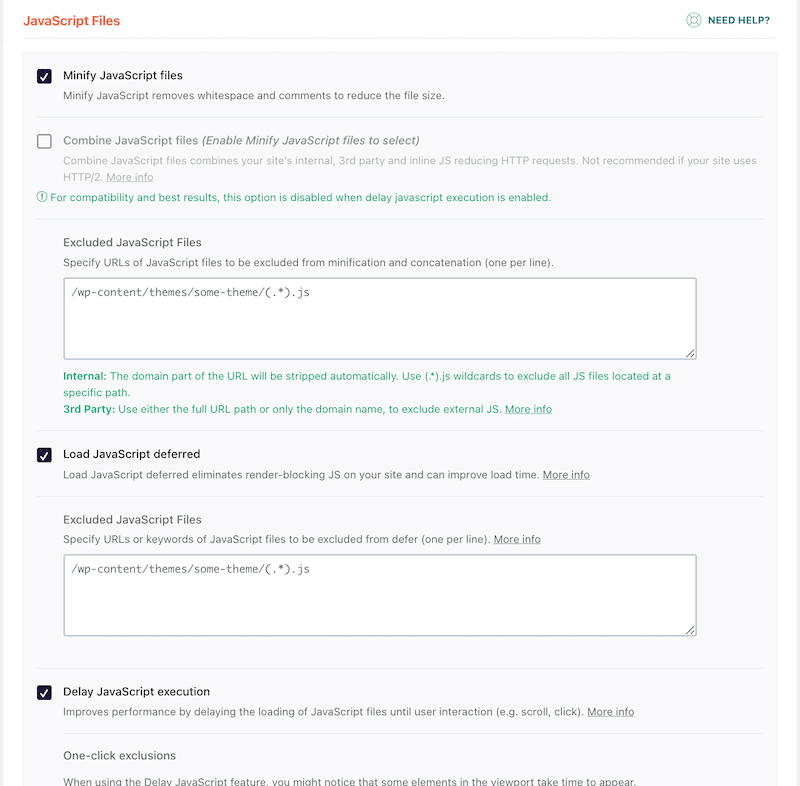
- Remove unused CSS to optimize CSS delivery:
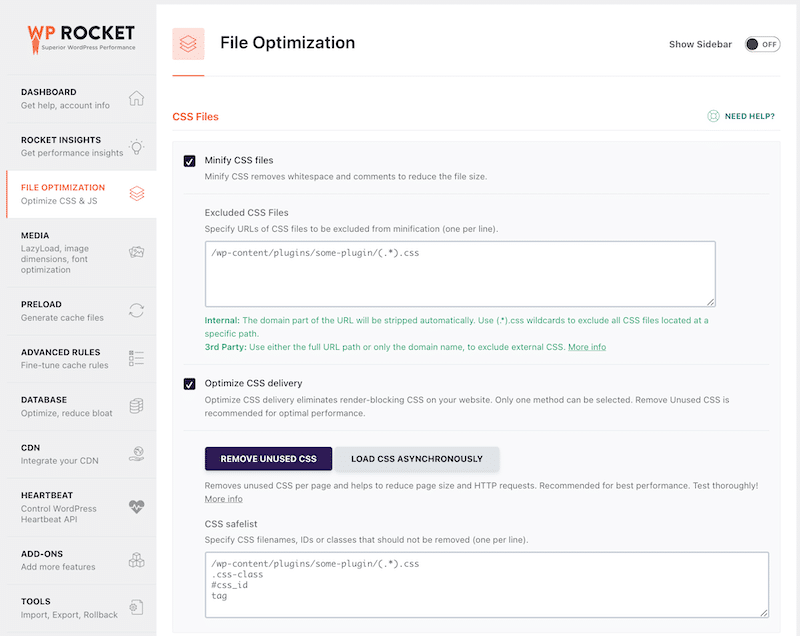
Step 3: Measuring Performance After Optimization (With WP Rocket)
After applying the optimizations, we run the same GTmetrix test again using the same location and settings. The performance results are much better!
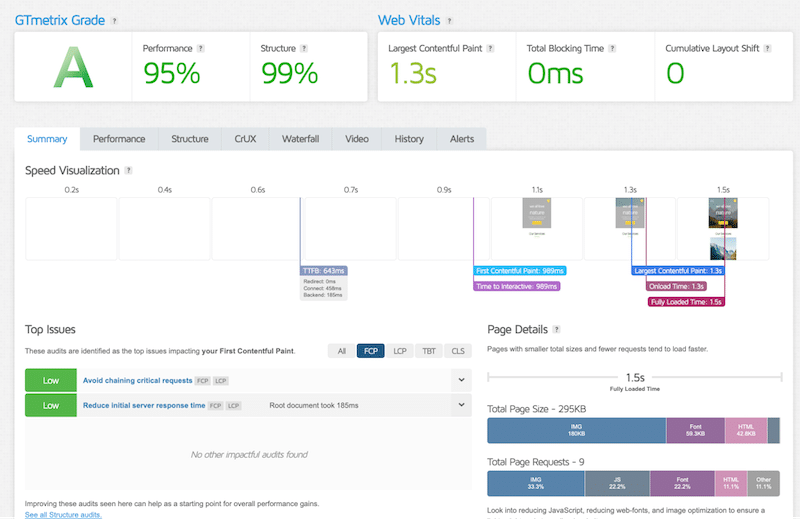
KPIs to record:
- Overall performance grade: A (95/100)
- Core Web Vitals (LCP and CLS): 1.3 s and 0
- Fully loaded time: 1.5s
- Page weight: 295 KB
Audits and recommendations:
WP Rocket fixed almost all the issues! There is still a bit of improvement to do to reduce initial server responsive time, but the impact is now low and in the green.
Key takeaways – How WP Rocket features helped improve website performance:
✅ Improved initial server response time with automatic caching.
✅ Sped up connections to external services with preconnect.
✅ Removed render-blocking resources by delaying and deferring JavaScript so content appeared faster.
✅ Reduced page size and improved rendering speed by removing unused CSS.
Comparison Table: How WP Rocket Helped to Easily Improve Website Performance
Here’s a visual comparison of website performance before and after optimization with WP Rocket and its impact on creating a fast-loading website:
| Metric | Before Optimization | After Optimization with WP Rocket 🚀 |
| Overall performance grade | C | A |
| LCP | 3.5s | 1.3s |
| CLS | 0 | 0 |
| Fully loaded time | 4.0s | 1.5s |
| Page weight | 473KB | 295KB |
8 Tips to Maintain Website Speed Over Time
Website speed optimization is not a one-time task. Every new image, plugin, update, or feature can affect performance if it is not monitored regularly. Use this simple checklist to keep your website fast and make website performance optimization part of your routine.
- Monitor Core Web Vitals over time to make sure user experience stays strong, and your site continues to meet Google’s performance signals.
Timeframe: Weekly, and you should set email alerts to monitor all the time.
- Test mobile performance on real 4G connections to make sure mobile visitors get a fast loading experience.
Timeframe: Weekly + one-time event if you add a lot of content or if you plan to run a promotion and expect a peak in traffic.
- Keep caching enabled at all times.
Timeframe: Always on (check performance after activation and important updates).
- Optimize every new image with Imagify to avoid adding heavy files to your pages.
Timeframe: Every time you upload new images.
- Remove unused plugins and external scripts using WP Rocket or Google Tag Manager to prevent unnecessary slowdowns.
Timeframe: Conduct the cleanup monthly.
- Keep your CMS, themes, and plugins up to date and retest your site speed after major updates.
Timeframe: Test after each major update.
- Clean unused CSS and delay JavaScript execution regularly with WP Rocket to keep pages lightweight.
Timeframe: Every 2 to 3 months, depending on how much content you add to your site.
- Review your hosting performance once a year and compare results with GTmetrix to ensure your server still meets your needs.
Timeframe: Every 6 months.
FAQ About Website Speed Optimization
What is website speed optimization?
Website speed optimization is the process of improving how fast your entire website loads and responds to users. It includes techniques such as caching, image optimization, code cleanup, content delivery networks (CDNs), and prioritizing important content to help visitors access pages quickly and smoothly.
What’s the difference between website speed and page speed?
Website speed refers to the overall performance of your entire site, including hosting, server response, and how pages load across different devices and locations. Page speed focuses on how fast a single page loads and becomes usable for visitors. Website speed optimization focuses on the big picture.
How fast should a website load?
Google recommends that a website should load in under 3 seconds. Ideally, your main content should appear even faster, especially on mobile devices.
What are the most common causes of slow websites?
The most common causes of slow websites include large unoptimized images, too many third-party scripts, heavy themes or plugins, missing caching, slow hosting, and unoptimized JavaScript and CSS files. Not prioritizing above-the-fold content can also make pages feel slow to users.
How often should I optimize website speed?
Website speed optimization should be an ongoing process, not a one-time task.
You should test your website performance regularly, especially after adding new content, installing plugins, or running updates. A weekly speed check is a good habit to maintain a fast-loading website over time.
Do plugins and tools really help improve website speed?
Yes, plugins and tools can significantly improve website speed when used correctly.
Performance tools like GTmetrix help you measure results, while optimization tools such as WP Rocket implement caching, code optimization, and many best practices.
Wrapping Up
Website speed optimization is one of the best investments you can make for your site’s success. A fast-loading website improves user experience, supports SEO, and helps you turn more visitors into customers. The key is to consistently follow website speed best practices: measure performance, fix the biggest bottlenecks, and keep your site optimized over time.
Common website speed optimization techniques include:
- Using fast and reliable hosting
- Making sure your theme and plugins do not slow down your site
- Optimizing images and media files
- Using caching
- Optimizing your JSS and CSS code
- Prioritizing the content that appears at the top of the screen, also called above-the-fold content.
If you use WordPress, WP Rocket makes this speed optimization process much easier. It applies 80% of the performance best practice upon activation, so you can improve website load times without touching code. And if you want to try it with zero stress, WP Rocket comes with a 14-day money-back guarantee, so you can test it on your own site and keep it only if you see real results!



