Table of Contents
Last update on
Soft 404s are fairly common errors that Google sometimes throws up for web pages, particularly for larger sites. They’re also a strange error because soft 404s are a hybrid of 404 and normal pages, and what exactly is causing this error for a particular page might not always be clear.
So in this post, I want to help clear up some of the confusion around why soft 404 errors happen, how they’re different from regular 404 errors, and how you can fix the SEO issues that cause them.
What is a Soft 404 Error?
“A soft 404 means that a URL on your site returns a page telling the user that the page does not exist and also a 200-level (success) code to the browser.”
Basically, you’ve got a page on your site telling visitors that it no longer exists, but at the same time, it’s telling search engines that it does exist.
Confusing, right?
In some cases, it might be a page on your site that doesn’t have much, if any, content. For example, WordPress automatically generates a new URL when you create a new tag for your site. If you’ve created a tag but haven’t yet published any posts using the tag, you’ll have an empty page on your site—and potentially a soft 404 on your hands.
So what’s really happening there? Well, these thin pages are super confusing for Googlebot. When it’s crawling your site and comes across a page that the server says exists but the content suggests otherwise, it thinks, “well, this page doesn’t offer any value to users so it’s not worth indexing” and gives it a soft 404 label.
It’s also possible to get a soft 404 when a page doesn’t exist and when a user lands on it after clicking through in search results, they’re redirect to a page that isn’t relevant to the search context. For example, the user lands on a page and is automatically redirected to the home page.
| 💡 Did you know? WP Rocket now includes Rocket Insights, the built-in performance tracking tool powered by GTmetrix. It brings hands-on monitoring right where you already optimize your website, so you can track your key pages, measure WP Rocket’s impact instantly, quickly spot and troubleshoot performance issues, and stay in control of your website performance without juggling multiple tools. 🚀 Update WP Rocket to the latest version to start using the Rocket Insights Free Plan right from your dashboard! |
Do Soft 404 Errors Really Matter?
When a web page returns a soft 404 error, it won’t appear in Google search. Basically, Google de-indexes pages that return a soft 404 error, which in turn can impact your SEO.
Let’s take a look at an example:
Let’s say you run an online store selling chairs and you’re having issues with one URL in particular: https://chairsgalorestore.com/products/sale/blue-chair
While your server might load the URL without issue, returning a 200 (OK) status code because there’s a real page at that URL, the content on the page could be telling visitors: “Sorry, there are no products matching your search.”
Basically, the page is displaying search results for a product that doesn’t exist because it’s no longer for sale or has sold out.
Ecommerce sites often contain dynamically generated pages and content that can throw up soft 404 errors when product lines sell out or are no longer available. Images: Unsplash.
This isn’t at all helpful for site visitors. After all, when they click through to your page from Google search, they are looking for blue chairs and are expecting to find blue chairs, but instead discover there aren’t any chairs available!
It’s for this reason why Google created the soft 404 error label—it’s a label, not an official HTTP response code—to deal with thin or non-existent content and ensure that only quality results appear in search.
So what happens to pages that get a soft 404? Google doesn’t index these pages.
Essentially, Google doesn’t want to waste its resources trying to crawl pages that send conflicting signals, no longer exist, or don’t offer valuable, quality content. So it simply removes them from its index and gets on with crawling pages that actually exist.
How to Check Your Site for Soft 404 Errors
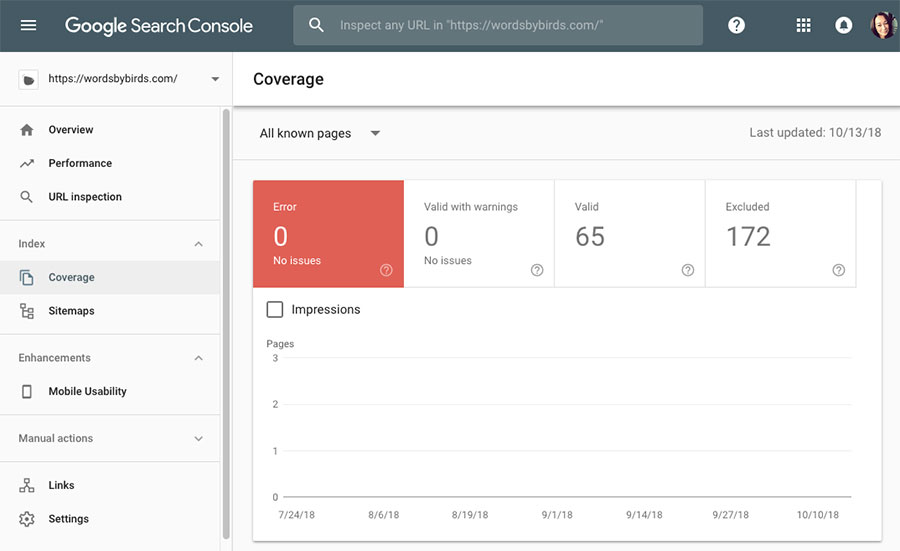
The easiest way to check for soft 404 errors is using Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools). Log in to your account and on the main screen you’ll see a graph for your site’s “Performance” (total clicks per day) and underneath will be a graph for “Coverage.”
If you have any pages with errors, including soft 404 errors, they’ll be displayed in the “Coverage” graph. Click “Open Report” for more details about your errors.
On the report screen, any errors will be displayed as a total in the big, red box. You can click this red error box to find out more about any errors on your site and what the source of the error might be.
Fortunately for me, as you can see on the Search Console screen for my website, I don’t have any errors that need fixing. However, this is the screen you would visit to find them.
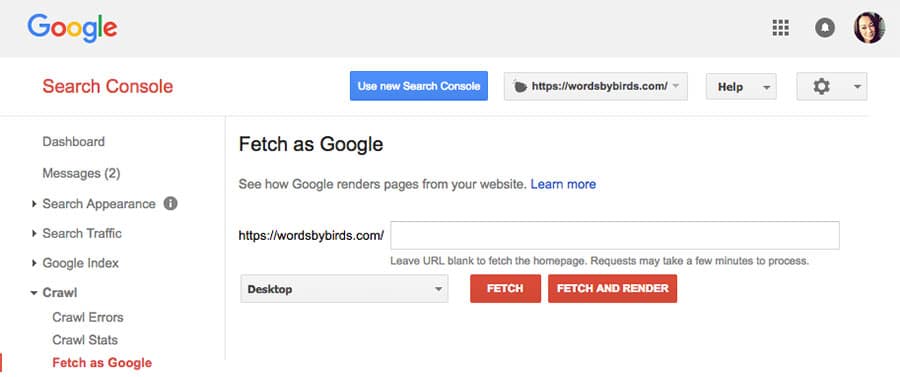
Alternatively, you can use Fetch as Google to check if a particular URL on your site is returning the correct status code, including soft 404 errors.
You can use this tool to see whether Googlebot can access the URL, how it renders the page, and whether any page resources (such as images or scripts) are blocked to Googlebot.
It simulates a crawl and render executive as done in Google’s normal crawling and rendering process, and is super useful for debugging crawl issues on your site.
How to Fix Soft 404 Errors
If you’re getting soft 404s on your site for critical pages, such as product, category, or lead generation pages, it’s crucial that you act quickly to fix these errors and get these pages indexed and back in Google search.
Likewise, if you have a large number of soft 404 errors relative to the total number of pages on your site, this is not a good look you’re sending Google. Too many soft 404 errors may lead to a reduced crawl rate of your site, which in turn could result to lower rankings and lead to fewer indexed pages—a big problem if you have hundreds or thousands of pages!
How you go about fixing soft 404 errors depends on the cause. But generally speaking, you should ensure the URL returns the right response code to match the actual content of the page.
Here are a few ways to fix soft 404 errors:
1. If the page is no longer available
Pages that no longer exist should return a 404 (not found) or 410 (gone) response code. Either code tells both browsers and search engines that the page no longer exists.
This can be a big problem for eCommerce stores and blogs, especially when you consider the three most common sources of soft 404 errors include:
- Empty search results pages
- Empty eCommerce product categories
- Empty blog categories
Since these pages are often dynamically generated and populated by WordPress, simply returning a hard 404 isn’t the best option.
What Google’s own guidelines suggest is in addition to returning a 404 response code, you should also display a custom 404 page that provides useful information to help visitors navigate your site. This might be a page listing your most popular pages, blog posts, or products.
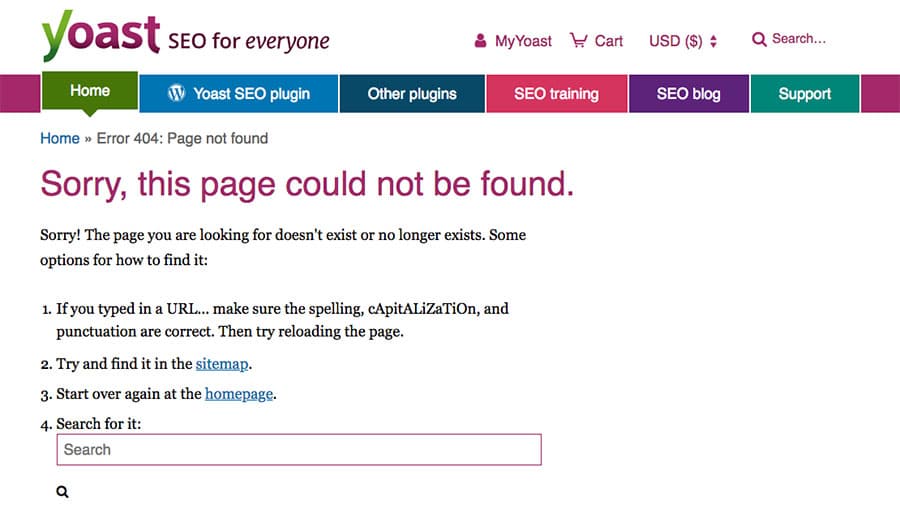
Yoast’s 404 page is a great example of how website’s can better serve lost users. Their 404 page clearly steps the use through how they can find what they’re looking for. And when you scroll down the page there are links to recent posts.
2. If the page has moved
If you’ve changed the URL for a page (e.g. updated the slug for a blog post) it should return a 301 (permanent redirect) and redirect users to the new URL.
Alternatively, if the page has moved because you’ve updated old content, you should redirect the URL to another page on your site containing up-to-date or more relevant information.
One of my favorite tools for setting up page redirects is the aptly named Redirection plugin. Alternatively, the premium version of Yoast SEO features a redirect manager.
3. If the page is available
If a page on your site is available and should be displaying in search results, it means Googlebot sees it as “thin” content. In this case, you need to work on improving the content on your page so you can avoid triggering a soft 404 error.
This means ensuring that when a user clicks through to your page from search results, your page delivers what they’re expecting. For example, to use my earlier example about shopping for blue chairs, you want to make sure that the page contains information about blue chairs that is informative and useful for the user.
4. If the page is available but you don’t want it to appear in Google search
There might be pages on your site getting soft 404 errors that you’d rather remove from Google’s index altogether. For example, you might have tag, category, or search results pages on your WordPress site that keep getting soft 404s and you’re not getting much SEO juice for these pages anyway.
In this case, you’ll need to tell Google not to crawl these pages. You can do this by adding disallow rules in your site’s robots.text file.
For search pages, for example, you could add the following lines to your robots.txt file:Disallow: /?s=Disallow: /search/
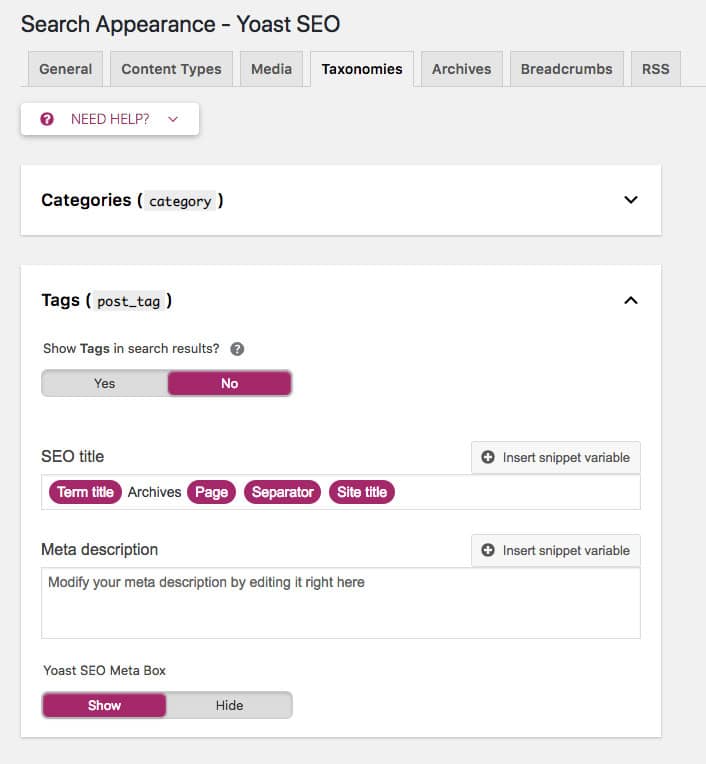
Alternatively, you could simply noindex pages you don’t want appearing in search results. The easiest way to do this is using the Yoast SEO plugin. By default, Yoast sets search pages and 404 pages to noindex, follow. But for tag and category pages you can add noindex rules in the “Search Appearance” tab.
Conclusion
Soft 404s are strange errors and it’s not always clear what’s causing them. But with a little digging around, especially in Google Search Console, you can get to the root of the problem and quickly implement a solution.
For WordPress sites in particular, which almost always have dynamically generated pages that throw up soft 404 errors, simply noindex these pages in Yoast’s settings. It’s also a good idea to have a custom 404 in place to catch users who land on pages that don’t exist so you can direct them to the important pages of your site.
It’s best to crawl your site regularly to check for any 404 or soft 404 errors and fix them quickly to keep the SEO health of your site in check. These are just a handful of ways that you can resolve soft 404 errors. If you have any other useful tips, let us know in the comments!